SSO with KeyCloak and Oauth2-Proxy
Centralized authentication and Single-Sign On can be implemented using Keycloak. Keycloak is an opensource Identity Access Management solution, providing centralized authentication and authorization services based on standard protocols and provides support for OpenID Connect, OAuth 2.0, and SAML.
sequenceDiagram
actor User
participant Keycloak
participant Application
User->>Application: User enters URL of an Application
Application->>Keycloak: Redirects to Keycloak
Keycloak->>User: Login page
User->>Keycloak: User gives credentials
Keycloak-->>Keycloak: Validates User
Keycloak->>Application: if Valid, Redirect to Application
Keycloak-->>User: Invalid credentials
-
Some of the GUIs of the Pi Cluster, Grafana, Kibana, Kiali, support SSO to be configured with an external IAM solution, delegating authentication to Keycloak instead of using local accounts.
Note:
Elasticsearch/Kibana SSO integration using OpenID Connect is not available in community edition. So, SSO won’t be configured for this component. Grafana SSO capability is enabled configuring OAuth2.0/OpenID Connect authentication. Follow instructions in Documentation: Monitoring (Prometheus) on how to integrate Grafana with Keycloak.
-
For those applications not providing any authentication capability (i.e. Longhorn, Prometheus, etc.), Ingress controller-based External Authentication can be configured. Ingress NGINX supports OAuth2-based external authentication mechanism using Oauth2-Proxy. See Ingress NGINX external Oauth authentication document Oauth2-proxy can be integrated with OpenId-Connect IAM, such us Keycloak.
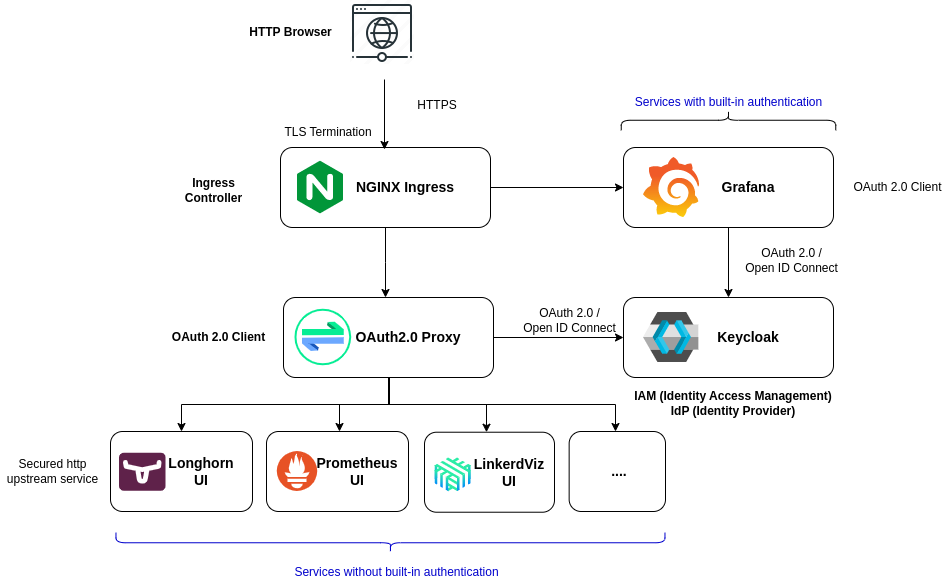
Keycloak
Installation using Bitnami Helm Chart
For installing Keycloak Bitnami’s helm chart will be used. This helm chart bootstraps a Keycloak deployment on Kubernetes using as backend a PostgreSQL database
-
Step 1: Add Bitnami Helm repository:
helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami -
Step 2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update -
Step 3: Create namespace
kubectl create namespace keycloak -
Step 4: Create file
keycloak-values.ymlglobal: storageClass: longhorn # Run in production mode behind NGINX proxy terminating TLS sessions production: true # ref: https://www.keycloak.org/server/reverseproxy proxyHeaders: xforwarded # Admin user auth: adminUser: admin # postgresSQL postgresql: enabled: true auth: username: keycloak database: keycloak # Ingress config ingress: enabled: true ingressClassName: "nginx" pathType: Prefix annotations: cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: ca-issuer # Increasing proxy buffer size to avoid # https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57503590/upstream-sent-too-big-header-while-reading-response-header-from-upstream-in-keyc nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffers-number: "4" nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: "16k" hostname: iam.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} tls: trueNote:
Substitute variables (
${var}) in the above yaml file before deploying helm chart.- Replace
${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}by the domain name used in the cluster. For example:homelab.ricsanfre.comFQDN must be mapped, in cluster DNS server configuration, to NGINX Ingress Controller’s Load Balancer service external IP. External-DNS can be configured to automatically add that entry in your DNS service.
With this configuration:
- Keycloak is deployed to run behind NGINX proxy terminating TLS connections.
proxyHeadersvariable need to be used. - PostgreSQL is deployed in standalone mode.
- Ingress resource is configured
Note: With this configuration all passwords Keycloak’s admin password and postgreSQL passwords are generated randomly. If helm chart is upgraded, it might cause issues generating a new passwords if the existing ones are not provided when executing helm upgrade command. See details in bitnami’s keycloak helm chart documentation: How to manage passwords
- Replace
- Step 5: Install Keycloak in
keycloaknamespacehelm install keycloak bitnami/keycloak -f keycloak-values.yml --namespace keycloak - Step 6: Check status of Keycloak pods
kubectl get pods -n keycloak -
Step 7: Get keycloak
adminuser passwordkubectl get secret keycloak -o jsonpath='{.data.admin-password}' -n keycloak | base64 -d && echo -
Step 8: connect to keycloak admin console
https://iam.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}Log in using ‘admin’ user and password obtained in step 7.
Alternative installation using external secret (GitOps)
Keycloak admin password and postgreSQL passwords can be provided during helm installation in values.yaml file. Alternatively, it can be provided in an external secret.
-
Step 1: Create secret containing admin password and posgresql passwords:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: keycloak-secret namespace: keycloak type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth data: admin-password: <`echo -n 'supersecret1' | base64`> postgresql-admin-password: <`echo -n 'supersecret2' | base64`> password: <`echo -n 'supersecret3' | base64`> -
Step 2: Add externalSecret to keycloak-values.yaml
# Admin user auth: existingSecret: keycloak-secret adminUser: admin # postgresSQL postgresql: enabled: true auth: username: keycloak database: keycloak existingSecret: keycloak-secret secretKeys: adminPasswordKey: postgresql-admin-password userPasswordKey: password architecture: standalone
Alternative installation using external database
Instead of using Bitnami’s PosgreSQL subchart, an external PosgreSQL database can be used. For example, using CloudNative-PG a, keycload database cluster can be created. See details on how to install CloudNative-PG in “Databases”.
-
Step 1. Create secret for keycloak admin user
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: keycloak-secret namespace: keycloak type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth data: admin-password: <`echo -n 'supersecret1' | base64`> -
Step 2. Create secret for external database
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: keycloak-db-secret namespace: keycloak labels: cnpg.io/reload: "true" type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth data: username: <`echo -n 'keycloak' | base64`> password: <`echo -n 'supersecret' | base64`> -
Step 1. Create CloudNative PG database for keycloak
apiVersion: postgresql.cnpg.io/v1 kind: Cluster metadata: name: keycloak-db namespace: keycloak spec: instances: 3 imageName: ghcr.io/cloudnative-pg/postgresql:16.3-4 storage: size: 10Gi storageClass: longhorn monitoring: enablePodMonitor: true bootstrap: initdb: database: keycloak owner: keycloak secret: name: keycloak-db-secret # Backup to external Minio (Optional) backup: barmanObjectStore: data: compression: bzip2 wal: compression: bzip2 maxParallel: 8 destinationPath: s3://k3s-barman/keycloak-db endpointURL: https://${S3_BACKUP_SERVER}:9091 s3Credentials: accessKeyId: name: keycloak-minio-secret key: AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID secretAccessKey: name: keycloak-minio-secret key: AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY retentionPolicy: "30d"Note: Substitute variables (
${var}) in the above yaml file before deploying helm chart.- Replace
${S3_BACKUP_SERVER}by FQDN of the Minio Backup server to be used. For example:s3.mydomain.com
- Replace
-
Step 3. Add external database configuration to helm values.yaml
# Admin user auth: existingSecret: keycloak-secret adminUser: admin # External DB: https://github.com/bitnami/charts/tree/main/bitnami/keycloak#use-an-external-database postgresql: enabled: false externalDatabase: host: "keycloak-db-rw" port: 5432 database: keycloak existingSecret: "keycloak-db-secret" existingSecretUserKey: "username" existingSecretPasswordKey: "password"
Automatic import of Realm configuration on startup
Realm configuration can be exported or imported to/from JSON files.
Once realm and clients are configured manually configuration can be exported to JSON file. See Keycloak export import configuration.
Realm configuration can be imported automatically from json file when deploying helm chart. See Importing realm on start-up
New ConfigMap, containing the JSON files to be imported need to be mounted by keycloak PODs as
/opt/bitnami/keycloak/data/import. --import-realm also need to be provided as extra arguments when starting the PODs.
-
Step 1: Create realm config map containing realm json files to be imported
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: keycloak-realm-configmap namespace: keycloak data: picluster-realm.json: | # JSON file -
Step 3: Apply configMap
kubectl apply -f keycloak-realm-configmap.yaml -
Step 2: Add to keycloak-values.yaml the following configuration and install helm char
# Importing realm on start-up # https://www.keycloak.org/server/importExport#_importing_a_realm_during_startup extraStartupArgs: "--import-realm" extraVolumes: - name: realm-config configMap: name: keycloak-realm-configmap extraVolumeMounts: - mountPath: /opt/bitnami/keycloak/data/import name: realm-config
Keycloak Operator
As an alteranative to Bitnami’s Helm Chart, Keycloak can be installed using Keycloak Operator. Keycloak Operator is an implementation of Kubernetes Operator design pattern enabling the definition of Keycloak deployment in a declarative way.
External DB creation
Follow previous steps described in Alternative Installation using External Database to deploy PosgreSQL database using CloudNative-PG operator and generate the secrets containing the database credentials
Keycloak Operator Installation
There is no official helm chart maintained by the community to install Keycloak Operator
It can be installed via manifest files which are in keycloak/keycloak-k8s-resources Github repository:
The installation process is the following:
- Install the CRDs by entering the following commands:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-k8s-resources/26.3.0/kubernetes/keycloaks.k8s.keycloak.org-v1.yml kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-k8s-resources/26.3.0/kubernetes/keycloakrealmimports.k8s.keycloak.org-v1.yml -
Install the Keycloak Operator deployment by entering the following command:
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-k8s-resources/26.3.0/kubernetes/kubernetes.yml
Note:
In the previous URLs replace version 26.3.0 by the latest Keycloak version available.
The Operator will watch the namespace where it is installed. You may optionally select a namespace with the -n option.
Kustomized package for Keycloak Operator
A Kustomize package can be created to install automatically the application.
keycloak-operator/
├── base
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ └── ns.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── prod
└── kustomization.yaml
-
keycloak-operator/base/kustomization.yamlapiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization namespace: keycloak resources: - ns.yaml - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-k8s-resources/26.3.0/kubernetes/keycloaks.k8s.keycloak.org-v1.yml - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-k8s-resources/26.3.0/kubernetes/keycloakrealmimports.k8s.keycloak.org-v1.yml - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-k8s-resources/26.3.0/kubernetes/kubernetes.yml -
keycloak-operator/base/ns.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Namespace metadata: name: keycloak -
keycloak-operator/overlays/prod/kustomization.yamlapiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization resources: - ../../base
Installing kustomize package application using the command:
kubectl kustomize keycloak-operator/overly/product | kubectl apply -f -
Keycloak Deployment
Keycloak CRD need to be applied to the kubernetes cluster, so Operator can deploy Keycloak.
Keycloak operator supports deployment of Keycloak in HA with several nodes of a single clusterr
The following creates a Keycloak server with the following options
- Initial admin bootstraping (
bootstrapAdmin) from an external secret - Enabling HTTP endpoint (
http.httpEnabled) and not configuring HTTPs. Keycloak running behind HTTP Proxy closing TLS sessions (Ingress Controller) - Disable creation of Ingress resource (
ingress.enabled). Ingress resource created by operator cannot be completely configured (TLS certificate cannot be added) - Keyclaok cluster of two instances (
instances)
and bootstrapping temporal admin user account
apiVersion: k8s.keycloak.org/v2alpha1
kind: Keycloak
metadata:
name: keycloak
namespace: keycloak
spec:
# Number of instances in the cluster
instances: 2
# External Database connection
db:
vendor: postgres
host: keycloak-db-rw
port: 5432
database: keycloak
usernameSecret:
name: keycloak-db-secret
key: username
passwordSecret:
name: keycloak-db-secret
key: password
# Bootstrap admin account
bootstrapAdmin:
user:
secret: keycloak
# Enabling HTTP communications
# Keycloak behing HTTP Proxy closing TLS connections
http:
httpEnabled: true
hostname:
hostname: https://iam.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}
strict: true
# Enabling back channel
backchannelDynamic: true
proxy:
headers: xforwarded # double check your reverse proxy sets and overwrites the X-Forwarded-* headers
# Do not create ingress
# TLS options are not supported. Ingress resource to be created separatedly.
ingress:
enabled: false
Bootstrapping admin account
A temporal admin account1 can be provided from a secret through spec.bootstrapAdmin
...
spec:
# Bootstrap admin account
bootstrapAdmin:
user:
secret: keycloak
Additional Options
Some expert server options are unavailable as dedicated fields in the Keycloak CR.
The spec.additionalOptions2 field of the Keycloak CR enables Keycloak to accept any available configuration in the form of key-value pairs.
You can use this field to include any option that is omitted in the Keycloak CR.
For details on configuring options, see Keycloak configuration reference guide.
The values can be expressed as plain text strings or Secret object references as shown in this example:
apiVersion: k8s.keycloak.org/v2alpha1
kind: Keycloak
metadata:
name: example-kc
spec:
# ...
additionalOptions:
- name: spi-connections-http-client-default-connection-pool-size
secret: # Secret reference
name: http-client-secret # name of the Secret
key: poolSize # name of the Key in the Secret
- name: spi-email-template-mycustomprovider-enabled
value: true # plain text value
Creating Ingress
Create Ingress resource for Keycloak so TLS sessions are closed in the Ingress Controller The following assumes NGINX Ingress Controller is used and TLS Certificate issue is automated with Cert-Manager
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: keycloak
namespace: keycloak
annotations:
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: ca-issuer
# Increasing proxy buffer size to avoid
# https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57503590/upstream-sent-too-big-header-while-reading-response-header-from-upstream-in-keyc
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffers-number: "4"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: "128k"
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx
tls:
- hosts:
- iam.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}
secretName: keycloak-tls-secret
rules:
- host: keycloak.localhost
http:
paths:
- backend:
service:
name: iam.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}
port:
name: http
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Important:
Only http port (8080) is exposed. Management port (9000) is not exposed
Keycloak Realm Import
Realm configuration can be imported also in a declarative way using Keycloak Operator3.
To import a realm, KeycloakRealmImport Kubernetes CRD has to be created:
Create keycloak-realm-import.yaml
apiVersion: k8s.keycloak.org/v2alpha1
kind: KeycloakRealmImport
metadata:
name: mycluster
namespace: keycloak
spec:
keycloakCRName: keycloak
realm:
<realm representation>
This CR should be created in the same namespace as the Keycloak Deployment CR, defined in the field keycloakCRName. The realm field accepts a full RealmRepresentation.
The recommended way to obtain a RealmRepresentation is by leveraging the export functionality Importing and Exporting Realms.
- Export the Realm to a single file.
-
Convert the JSON file to YAML.
Tip: Conversion can be done automatically with
yqtoolsudo apt install yq cat realm.json | yq -y -
Copy and paste the obtained YAML file as body for the
spec.realmkey in KeycloakrRealmImport manifest, making sure the indentation is correct. -
Apply the changes:
kubectl apply -f keycloak-realm-import.yaml -
To check the status of the running import, enter the following command:
kubectl get keycloakrealmimports/mycluster -o go-template='{{range .status.conditions}}CONDITION: {{.type}}{{"\n"}} STATUS: {{.status}}{{"\n"}} MESSAGE: {{.message}}{{"\n"}}{{end}}'
Realm Import Limitations
- If a Realm with the same name already exists in Keycloak, it will not be overwritten.
- The Realm Import CR only supports creation of new realms and does not update or delete those. Changes to the realm performed directly on Keycloak are not synced back in the CR
After testing the functionality additional limitation has been discovered:
- Client Scopes import is not working as expected (default Client Scopes are not present after doing the import of only new client scopes)
| Resource | Test Status | Result |
|---|---|---|
| client | ✅ | Defined Clients are added to default clients (added by default when creating a new realm): account, broker, account-console, etc. |
| client-roles | ✅ | New Client roles are added properly to the corresponding client. |
| users | ✅ | Users added. Default realm creation does not create any users |
| groups | ✅ | Groups added. Default realm creation does not create any group |
| clientScopes | ❌ | Only client scopes included in the json realm are imported. Default client-scopes, created by default when creating a new realm are deleted |
Note: For importing realm configuration using GitOps paradigm, better use keycloak-config-cli tool see section below.
This tools support import/re-import of configuration including the support for importing clientScopes without purging the existing ones.
Keycloak Configuration
Manual Configuration
-
Step 1: Login as admin to Keycloak console
Open URL:
https://iam.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} -
Step 2: Create a new realm
piclusterFollow procedure in Keycloak documentation:Keycloak: Creating a Realm
-
Step 3: Start on-boarding applications
For configuring Grafana’s application in Keycloak to enable SSO, follows steps described in “Grafana Installation - Configuring SSO”
For configuration OAuth Proxy authentication middleware follow steps described below
-
Step 4: Create user
Admin user:
piadmincan be created manually and assigning the required roles of the different applications.Follow procedrure in Keycloak documentation: Keycoak: Managing Users
Automating configuration changes with keycloak-config-cli
keycloak-config-cli is a Keycloak utility to ensure the desired configuration state for a realm based on a JSON/YAML file. It can be used to apply GitOps and IaC (Infrastructure as Code) concepts to Keycloak configuration
The config files are based on the keycloak export files, and they can be used to import or update Keycloak configuration without having to restart Keycloak.
keyclaok-config-cli utility can be executed in Kubernetes environment as a Job.
The kubernetes application can be packaged using kustomize
keycloak-config-cli
├── base
│ ├── config
│ │ ├── 01-realm.json
│ │ ├── 02-clients.json
│ │ ├── 03-groups.json
│ │ └── 04-users.json
│ ├── job.yaml
│ ├── kc-config-cli-env-secret.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── prod
└── kustomization.yaml
Where base/config directory stores the keycloak configuration files in json format. keycloak-config-cli will be configured to import all files in sequence order
keycloak-config-cli/base/kustomization.yamlapiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization namespace: keycloak configMapGenerator: # Generate keycloak config realm - name: keycloak-realm-configmap files: - config/01-realm.json - config/02-clients.json - config/03-groups.json - config/04-users.json resources: - kc-config-cli-env-secret.yaml - job.yamlKustomize application automatically generates a configMap
kecloak-realm-configmapcontaining the keyclaok configuration json files. This configMap will be automatically mounted by the POD running the Kubernetes Job to import the configuration-
keycloak-config-cli/base/kc-config-cli-env-secret.yamlSecret containing environment variables that will be used by
keycloak-config-cli.apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: kc-config-cli-secret namespace: keycloak stringData: KEYCLOAK_ADMIN: admin KEYCLOAK_PASSWORD: supersecret -
keycloak-config-cli/base/job.yamlapiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: keycloak-import-realm labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: keycloak-config-cli spec: backoffLimit: 1 template: metadata: labels: app.kubernetes.io/name: keycloak-config-cli spec: restartPolicy: Never containers: - name: keycloak-config-cli image: "docker.io/adorsys/keycloak-config-cli:6.4.0-26.1.0" imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent env: - name: "IMPORT_PATH" value: "/config/" - name: "KEYCLOAK_URL" value: "http://keycloak-service:8080" # Enable variable substitution - name: "IMPORT_VARSUBSTITUTION_ENABLED" value: "true" - name: "CLUSTER_DOMAIN" value: ${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} - name: "PI_ADMIN_FIRSTNAME" value: ${PI_ADMIN_FISTNAME} - name: "PI_ADMIN_LASTNAME" value: ${PI_ADMIN_LASTNAME} # Additional environment variables in secret envFrom: - secretRef: name: kc-config-cli-env volumeMounts: - name: config mountPath: /config volumes: - name: config configMap: name: "keycloak-realm-configmap" defaultMode: 0555The following environment variables are configured
KEYCLOAK_URL: Endpoint where keycloak service is accesibleIMPORT_VARSIBSTITUTION_ENABLED: So variables defined within json configuration files can be substituted before importing the filesIMPORT_PATH: Path where the config files to be imported are located. Pointing to ConfigMap mount point.
Additional environment variables are provided by
kc-config-cli-envSecret.KEYCLOAK_USERandKEYCLOAK_PASSWORDKeycloak admin user and password.
Also any variable used in configuration json files need to be provided to the POD.
-
keycloak-config-cli/overlays/prod/kustomization.yamlapiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization resources: - ../../base
The following keycloak config files can be used to configure automatically Keycloak
-
keycloak-config-cli/base/config/01-realm.json. Used to create a new realmpicluster{ "enabled": true, "realm": "picluster" } -
keycloak-config-cli/base/config/04-clients.json. Containing configuration of different client applications (grafana, oauth-proxy, etc.)As example, oauth2-proxy application can be automatically imported with the following:
{ "enabled": true, "realm": "picluster", "clients": [ { "clientId": "$(env:PROXY_OAUTH_CLIENT_ID)", "name": "Proxy OAuth 2.0", "description": "Proxy OAuth 2.0", "surrogateAuthRequired": false, "enabled": true, "clientAuthenticatorType": "client-secret", "secret": "$(env:PROXY_OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET)", "redirectUris": [ "https://oauth2-proxy.$(env:CLUSTER_DOMAIN)/oauth2/callback" ], "webOrigins": [ "https://oauth2-proxy.$(env:CLUSTER_DOMAIN)" ], "standardFlowEnabled": true, "directAccessGrantsEnabled": false, "protocol": "openid-connect", "protocolMappers": [ { "name": "aud-mapper-proxy-oauth2", "protocol": "openid-connect", "protocolMapper": "oidc-audience-mapper", "consentRequired": false, "config": { "included.client.audience": "$(env:PROXY_OAUTH_CLIENT_ID)", "id.token.claim": "true", "access.token.claim": "true" } } ], "defaultClientScopes": [ "web-origins", "acr", "roles", "profile", "email" ], "optionalClientScopes": [ "address", "phone", "offline_access", "microprofile-jwt" ], "access": { "view": true, "configure": true, "manage": true } } ] }keycloak-config-cli pod has to be executed with environment variables containing client application credentials (
PROXY_OAUTH_CLIENT_IDandPROXY_OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET) and cluster services base DNS domain (CLUSTER_DOMAIN) -
keycloak-config-cli/base/config/03-groups.json. Used to create aadminof users, with roles in differente applications (example :grafana admins){ "enabled": true, "realm": "picluster", "groups": [ { "name": "admin", "path": "/admin", "subGroups": [], "attributes": {}, "realmRoles": [], "clientRoles": { "grafana": [ "admin" ] } } ] } -
keycloak-config-cli/base/config/04-users.json. Used to create apiadminuser, belonging toadmingroup. All attributes of the user can be provided to keycloak-config-cli as environment variables (PI_ADMIN_USERNAME,PI_ADMIN_FIRSTNAME,PI_ADMIN_LAST_NAME,PI_ADMIN_PASSWORD, etc.){ "enabled": true, "realm": "picluster", "users": [ { "username": "$(env:PI_ADMIN_USERNAME)", "firstName": "$(env:PI_ADMIN_FIRSTNAME)", "lastName": "$(env:PI_ADMIN_LASTNAME)", "email": "admin@$(env:CLUSTER_DOMAIN)", "enabled": true, "emailVerified": true, "credentials": [ { "type": "password", "value": "$(env:PI_ADMIN_PASSWORD)" } ], "realmRoles": [ "default-roles-picluster" ], "groups": [ "admin" ] } ] }
To execute configuration import:
kubectl kustomization keycloak-config-cli/overlays/prod | kubectl apply -f -
Note: About re-executing the import job
Attempting to update the Job manifest after it has been applied to the cluster will not be allowed, as changes to the Job spec.Completions, spec.Selector and spec.Template are not permitted by the Kubernetes API. To be able to update a Kubernetes Job, the Job has to be recreated by first being removed and then reapplied to the cluster.
In case of integrating with GitOps tool, like FluxCD, the following annotation need to be added to the job, so FluxCD will automatically recreate it whenever there are changes to be applied: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/force: enabled
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: keycloak-import-realm
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: keycloak-config-cli
annotations:
# Update the Job manifest after it has been applied to the cluster is not allowed:
# - changes to the Job spec.Completions, spec.Selector and spec.Template are not permitted by the Kubernetes API (inmutable fields)
# Force recreation of the Job
# Kubernetes does not allow to patch Jobs
# Ref: https://fluxcd.io/flux/use-cases/running-jobs/
# Ref: https://fluxcd.io/flux/components/kustomize/kustomizations/#force
kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/force: enabled
spec:
# ...
Keycloak Observability
Metrics
Keycloak exposes Prometheus-format metrics at the following endpoint on the management interface (default TCP port 9000) at /metrics.
See details on how to enable the metrics in Keycloak documentation: Observability Configuring Metrics. Keycloak metrics description can be found in Keycloak documentation: Observability Metrics for Troubleshooting.
To enable Prometheus’ /metric endpoint (management interface) add the following additionalOptions to Keycloak resource
spec:
additionalOptions:
# Enable metrics endpoint
- name: metrics-enabled
value: 'true'
Important: Management port (:9000) should not be exposed externally.
Additional options can be provided to enable additional metrics
spec:
additionalOptions:
# Enable metrics endpoint
- name: metrics-enabled
value: 'true'
# Enable cache metrics histograms
- name: cache-metrics-histograms-enabled
value: 'true'
# Enable HTTP request histograms
- name: http-metrics-histograms-enabled
value: 'true'
# Enable user metrics
- name: event-metrics-user-enabled
value: 'true'
| parameter | VAR | Description | value |
|---|---|---|---|
metrics-enabled |
KC_METRICS_ENABLE |
Enable metrics endpoint | true/false (default) |
cache-metrics-histograms-enabled |
KC_CACHE_METRICS_HISTOGRAMS_ENABLED |
Enable histograms for metrics for the embedded caches. | true/false(default) |
http-metrics-histograms-enabled |
KC_HTTP_METRICS_HISTOGRAMS_ENABLED |
Enables a histogram with default buckets for the duration of HTTP server requests. | true/false(default) |
event-metrics-user-enabled |
KC_EVENT_METRICS_USER_ENABLED |
Create metrics based on user events4. | true, false (default) |
Prometheus Integration
ServiceMonitoring, Prometheus Operator’s CRD, resource can be automatically created so Kube-Prometheus-Stack is able to automatically start collecting metrics from Keycloak.
Apply following manifest:
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
name: keycloak-service-monitor
namespace: keycloak
spec:
endpoints:
- interval: 30s
path: /metrics
port: management
selector:
matchLabels:
app: keycloak
Grafana dashboards
Keycloak provides Grafana Dashboards to display metrics collected by Prometheus. They are available at keycloak/keycloak-grafana-dashboard Github repo.
There are 2 Dashboards available:
Find further details in Keycloak documentation: Observability Grafana Dashboards
Dashboard can be automatically added using Grafana’s dashboard providers configuration. See further details in “PiCluster - Observability Visualization (Grafana): Automating installation of community dasbhoards
Add following configuration to Grafana’s helm chart values file, so a Keycloak’s dashboard provider can be created and dashboards can be automatically downloaded from GitHub repository
dashboardProviders:
dashboardproviders.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
providers:
- name: keycloak
orgId: 1
folder: Keycloak
type: file
disableDeletion: false
editable: true
options:
path: /var/lib/grafana/dashboards/keycloak-folder
# Dashboards
dashboards:
keycloak:
keycloak-planning:
url: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-grafana-dashboard/refs/heads/main/dashboards/keycloak-capacity-planning-dashboard.json
datasource:
- { name: DS_PROMETHEUS, value: Prometheus }
keycloak-troubleshooting:
url: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/keycloak/keycloak-grafana-dashboard/refs/heads/main/dashboards/keycloak-troubleshooting-dashboard.json
datasource:
- { name: DS_PROMETHEUS, value: Prometheus }
Proxy Oauth 2.0
Configure Oauth2-Proxy Client in Keycloak
OAuth2-Proxy client application need to be configured within ‘picluster’ realm.
Procedure in Keycloak documentation: Keycloak: Creating an OpenID Connect client
Follow procedure in Oauth2-Proxy: Keycloak OIDC Auth Provider Configuration to provide the proper configuration.
-
Step 1: Create a new OIDC client in ‘picluster’ Keycloak realm by navigating to: Clients -> Create client
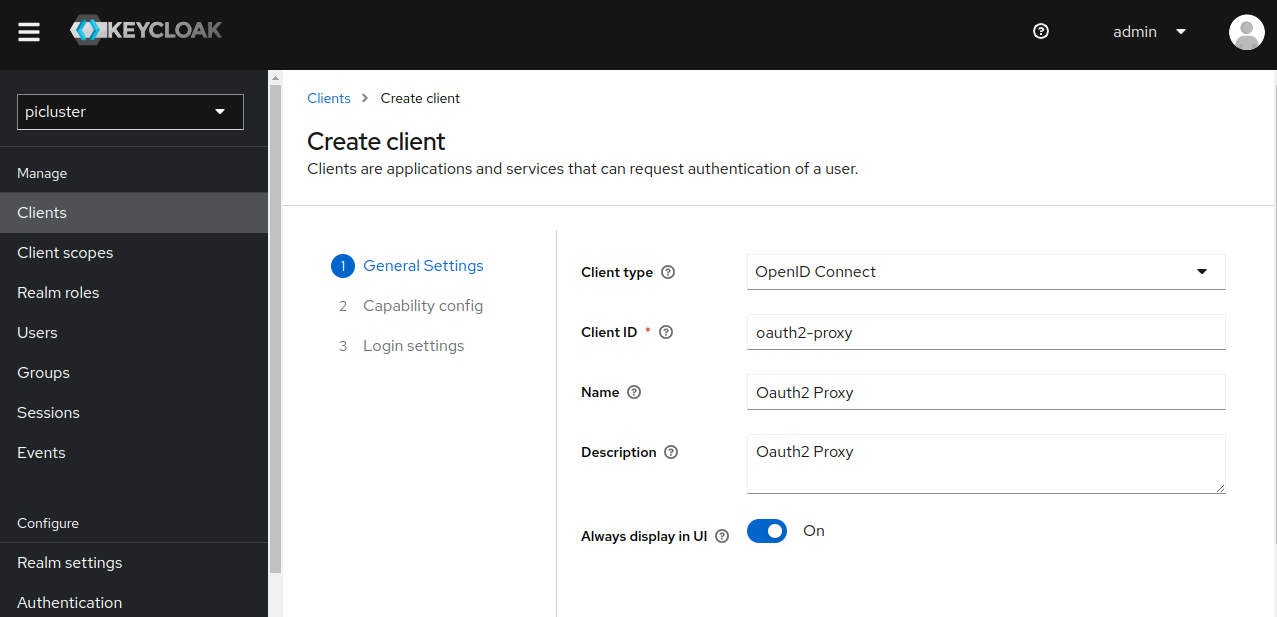
- Provide the following basic configuration:
- Client Type: ‘OpenID Connect’
- Client ID: ‘oauth2-proxy’
- Click Next.
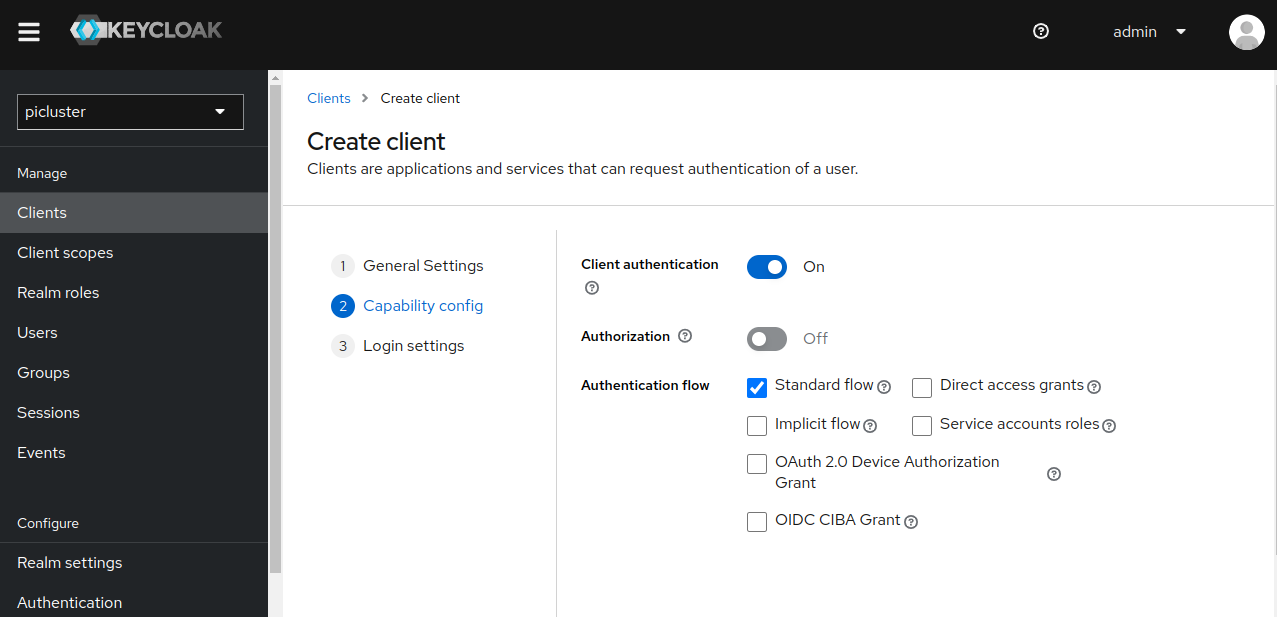
- Provide the following ‘Capability config’
- Client authentication: ‘On’
- Authentication flow
- Standard flow ‘selected’
- Direct access grants ‘deselect’
- Click Next
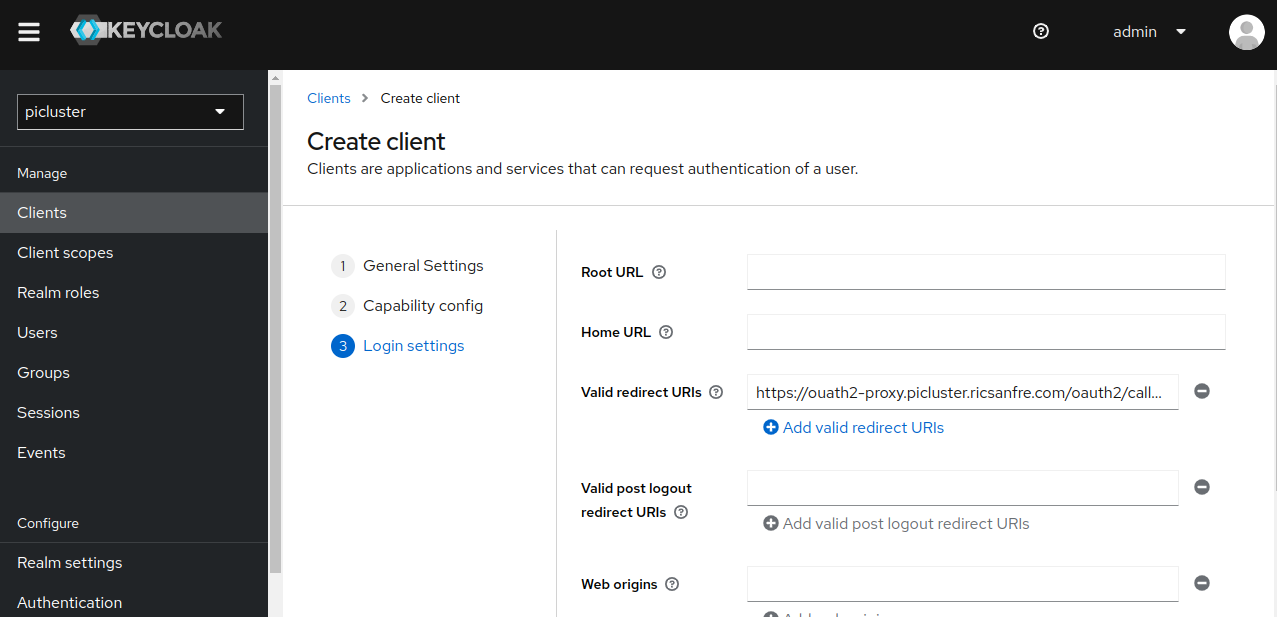
- Provide the following ‘Logging settings’
- Valid redirect URIs:
https://ouath2-proxy.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}/oauth2/callback
- Valid redirect URIs:
- Save the configuration.
- Provide the following basic configuration:
-
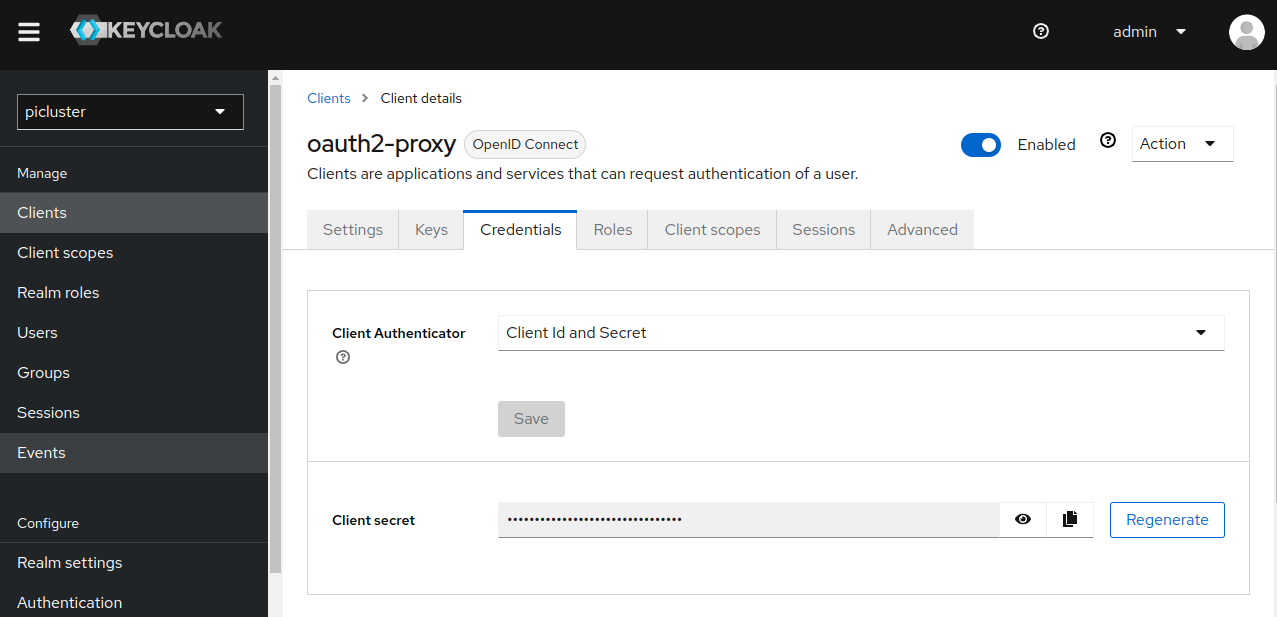
Step 2: Locate oauth2-proxy client credentials
Under the Credentials tab you will now be able to locate oauth2-proxy client’s secret.
-
Step 3: Configure a dedicated audience mapper for the client
-
Navigate to Clients -> oauth2-proxy client -> Client scopes.
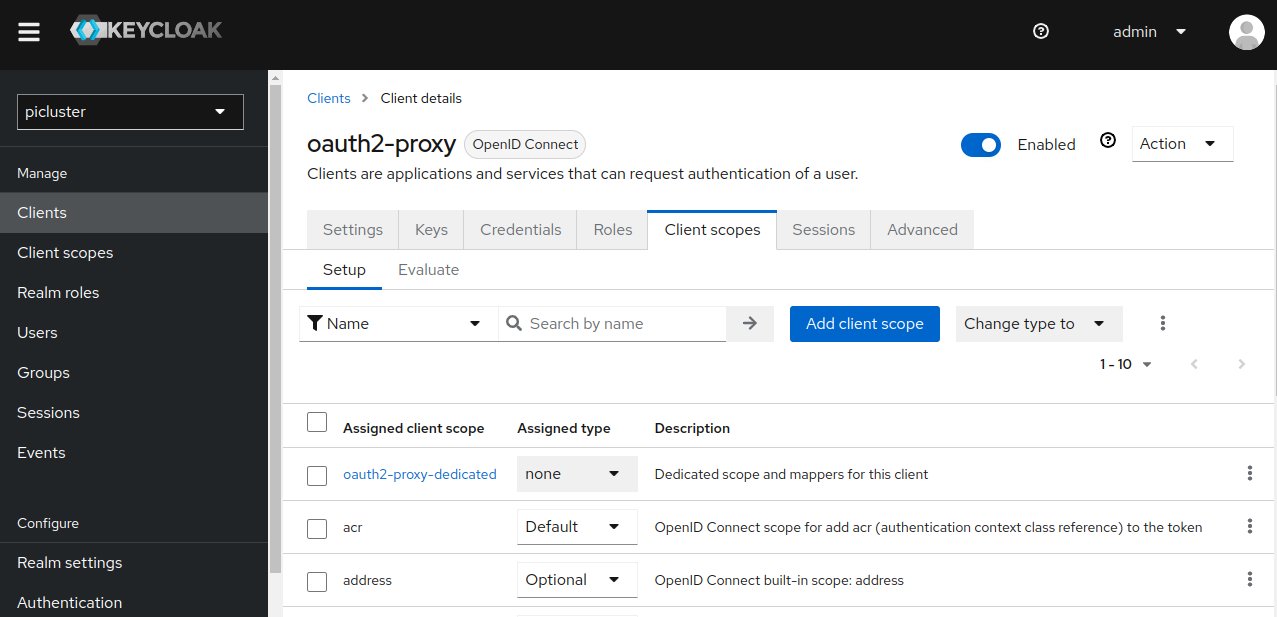
- Access the dedicated mappers pane by clicking ‘oauth2-proxy-dedicated’, located under Assigned client scope. (It should have a description of “Dedicated scope and mappers for this client”)
-
Click on ‘Configure a new mapper’ and select ‘Audience’
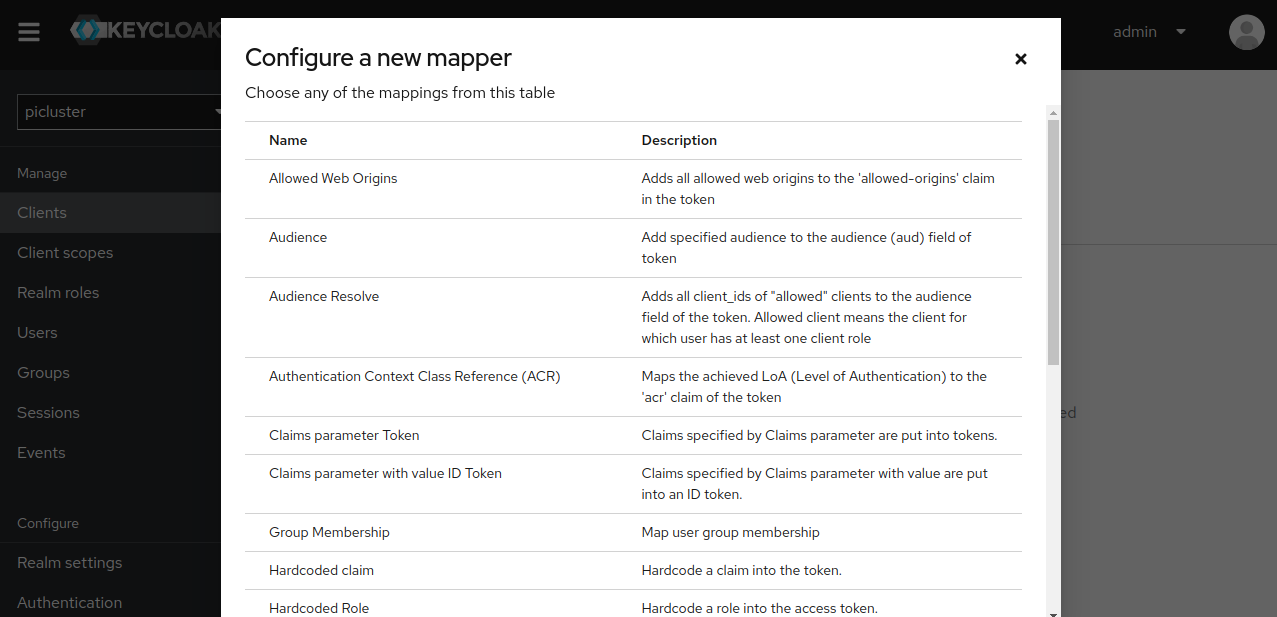
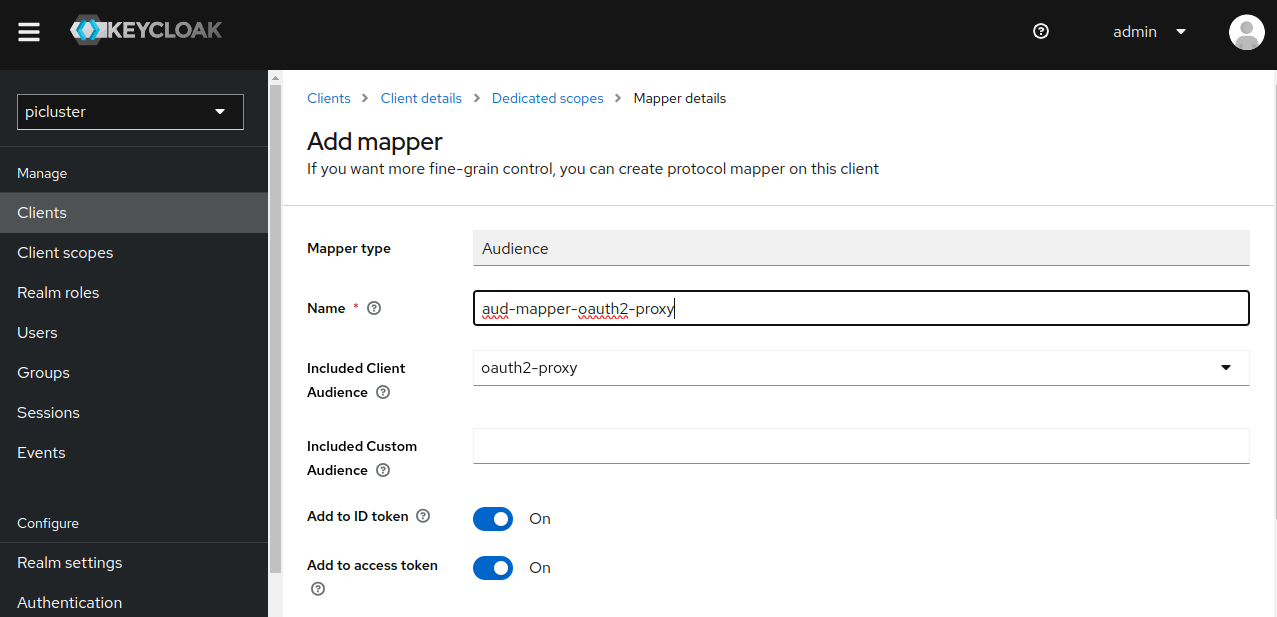
- Provide following data:
- Name ‘aud-mapper-oauth2-proxy’
- Included Client Audience select oauth2-proxy client’s id from the dropdown.
- Add to ID token ‘On’
- Add to access token ‘On’ OAuth2 proxy can be set up to pass both the access and ID JWT tokens to your upstream services.
- Save the configuration.
-
OAuth2 Proxy Installation
-
Step 1: Add Helm repository:
helm repo add oauth2-proxy https://oauth2-proxy.github.io/manifests -
Step 2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update -
Step 3: Create namespace
kubectl create namespace oauth2-proxy -
Step 4: Create file
oauth2-proxy-values.ymlconfig: # Add config annotations annotations: {} # OAuth client ID # Follow instructions to configure Keycloak client # https://oauth2-proxy.github.io/oauth2-proxy/configuration/providers/keycloak_oidc # Oauth2 client configuration. From Keycloak configuration clientID: "oauth2-proxy" clientSecret: "supersecreto" # Cookie secret # Create a new secret with the following command # openssl rand -base64 32 | head -c 32 | base64 cookieSecret: "bG5pRDBvL0VaWis3dksrZ05vYnJLclRFb2VNcVZJYkg=" # The name of the cookie that oauth2-proxy will create # If left empty, it will default to the release name cookieName: "oauth2-proxy" # Config file configFile: |- # Provider config provider="keycloak-oidc" provider_display_name="Keycloak" redirect_url="https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}/oauth2/callback" oidc_issuer_url="https://iam.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}/realms/picluster" code_challenge_method="S256" ssl_insecure_skip_verify=true # Upstream config http_address="0.0.0.0:4180" upstreams="file:///dev/null" email_domains=["*"] cookie_domains=["${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}"] cookie_secure=false scope="openid" whitelist_domains=[".${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}"] insecure_oidc_allow_unverified_email="true" sessionStorage: # Can be one of the supported session storage cookie|redis type: redis # Enabling redis backend installation redis: enabled: true # standalone redis. No cluster architecture: standalone ingress: enabled: true className: "nginx" pathType: Prefix path: /oauth2 annotations: # Enable cert-manager to create automatically the SSL certificate and store in Secret # Possible Cluster-Issuer values: # * 'letsencrypt-issuer' (valid TLS certificate using IONOS API) # * 'ca-issuer' (CA-signed certificate, not valid) cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-issuer cert-manager.io/common-name: oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: "16k" hosts: - oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} tls: - hosts: - oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} secretName: oauth2-proxy-tlsNote:
Substitute variables (
${var}) in the above yaml file before deploying helm chart.- Replace
${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}by the domain name used in the cluster. For example:homelab.ricsanfre.com
-
Step 5: Install helm chart
helm install oauth2-proxy oauth2-proxy/oauth2-proxy -f oauth2-proxy-values.yml --namespace oauth2-proxy -
Step 6: Check status oauth2-proxy PODs
kubectl --namespace=oauth2-proxy get pods -l "app=oauth2-proxy"
- Replace
Alternative installation using external secret (GitOps)
OAuth credentials (clientID, client secret), cookie secret and redis password can be provided from external secret
Tip: About ArgoCD and helm native commands
Redis backend is installed using redis bitnami helm sub-chart. This helm chart creates a random credential for redis backend.
When using ArgoCD, helm native commands, like random or lookup, used by the helm chart for generating this random secret are not supported and so oauth2-proxy fails to save any data to redis.
See issue bitnami@charts#18130 and issue argocd@argocd#14944
As workaround, the issue can be solved providing the credentials in a external secrets.
-
Step 1: Create secret containing oauth2-proxy credentials:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: oauth2-proxy-secret namespace: oauth2-proxy type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth data: client-id: <`echo -n 'oauth2-proxy' | base64`> client-secret: <`echo -n 'supersecret | base64`> cookie-secret: <`openssl rand -base64 32 | head -c 32 | base64`> redis-password: <`openssl rand -base64 32 | head -c 32 | base64`>client-secret value should be taken from Oauth2-proxy client configuration
-
Step 2: Add existingSecret to oauth2-proxy-values.yaml and install helm chart
# Admin user auth: existingSecret: oauth2-proxy-secret # clientID: "oauth2-proxy" # clientSecret: "supersecreto" # cookieSecret: "bG5pRDBvL0VaWis3dksrZ05vYnJLclRFb2VNcVZJYkg=" sessionStorage: type: redis redis: existingSecret: oauth2-proxy-secret passwordKey: redis-password redis: enabled: true # standalone redis. No cluster architecture: standalone # Get redis password from existing secret using key redis-password auth: existingSecret: oauth2-proxy-secret existingSecretPasswordKey: redis-password
Configuring Ingress external authentication
Following annotations need to be added to any Ingress resource to use Oauth2-proxy authentication
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-signin: https://oauth2-proxy.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}/oauth2/start?rd=https://$host$request_uri
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: http://oauth2-proxy.oauth2-proxy.svc.cluster.local/oauth2/auth
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: "16k"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-response-headers: Authorization
Note:
Replace ${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} by the domain name used in the cluster.