Ansible Control Node
My laptop running Ubuntu desktop will be used as Ansible Control Node.
As an alternative a Virtual-BOX VM running on a Windows PC can be used as Ansible Control Node, pimaster for automating the provisioning of the Raspberry PIs cluster.
As OS for pimaster a Ubuntu 20.04 LTS or 22.04 LTS server can be used.
Tip:
This server, pimaster, can be automatically provisioned as a Virtual Box VM in a Windows Laptop using a ubuntu cloud image using the procedure described in Github repository ubuntu-clod-vbox.
Using that provisioning script a cloud-init user-data booting file can be created to automate the installation tasks of all component needed (Docker, Vagrant, KVM, Ansible, etc.). Check this template as an example.
Installing Ansible Runtime Environment
Docker is used to build an Ansible Runtime environment, a single docker image containing all ansible packages and its dependencies for executing the automation workflows.
Installing Docker
Follow official installation guide.
-
Step 1. Uninstall old versions of docker
for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done -
Step 2. Install packages to allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install \ apt-transport-https \ ca-certificates \ curl \ gnupg \ lsb-release -
Step 3. Add docker´s official GPG key
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc -
Step 4: Add x86_64 repository
echo \ "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \ $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null -
Step 5: Install Docker Engine
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -
Step 6: Enable docker management with non-priviledge user
-
Create docker group
sudo groupadd docker -
Add user to docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
-
-
Step 7: Configure Docker to start on boot
sudo systemctl enable docker.service sudo systemctl enable containerd.service -
Step 8: Configure docker daemon.
-
Edit file
/etc/docker/daemon.jsonSet storage driver to overlay2 and to use systemd for the management of the container’s cgroups. Optionally default directory for storing images/containers can be changed to a different disk partition (example /data). Documentation about the possible options can be found here
{ "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"], "log-driver": "json-file", "log-opts": { "max-size": "100m" }, "storage-driver": "overlay2", "data-root": "/data/docker" } -
Restart docker
sudo systemctl restart docker
-
Creating ansible-runner docker environment
The following directory/files structure is needed for the ansible runtime environment (ansible-runner)
📁
├── 📁 ansible-runner
│ ├── 📁 build
│ │ ├── requirements.txt
│ │ └── requirements.yml
│ ├── 📁 certbot
│ │ ├── 📁 config
│ │ ├── 📁 log
│ │ └── 📁 work
│ ├── docker-compose.yaml
│ ├── Dockerfile
│ └── 📁 runner
│ ├── 📁 .ssh
│ ├── 📁 .vault
│ ├── 📁 .gnugp
│ └── 📁 scripts
│ ├── generate_gpg_key.sh
│ └── generate_vault_password.sh
├──📁 ansible
├── ansible.cfg
├── inventory.yml
├── 📁 roles
Where:
ansible-runnerdirectory contains docker image building and running files and host directories mounted as volumes when running the docker containeransibledirectory contains typical directory structure of an ansible project
Ansible-runner docker image
This docker image contains all packages needed for running ansible and bootstraping the cluster.
├── 📁 build
│ ├── requirements.txt
│ └── requirements.yml
│ └── ansible_runner_setup.yml
├── Dockerfile
Dockerfile:
FROM ghcr.io/helmfile/helmfile:v0.167.1 AS helmfile
FROM python:slim
ARG ANSIBLE_GALAXY_CLI_COLLECTION_OPTS=--ignore-certs
ARG ANSIBLE_GALAXY_CLI_ROLE_OPTS=--ignore-certs
RUN apt-get update -qq && \
apt-get install sudo git apt-utils python3-pip pwgen gnupg -y && \
apt-get clean && \
rm -rf /usr/share/doc/* /usr/share/man/* /var/lib/apt/lists/* /tmp/* /var/tmp/*
# Intall basic Python packages
RUN pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools
RUN pip3 install ansible-core ansible-runner certbot
ADD build /build
WORKDIR /build
# Install python dependencies
RUN pip3 install -r requirements.txt
# Install ansible roles/collections dependencies
RUN ansible-galaxy role install $ANSIBLE_GALAXY_CLI_ROLE_OPTS -r requirements.yml --roles-path "/usr/share/ansible/roles"
RUN ANSIBLE_GALAXY_DISABLE_GPG_VERIFY=1 ansible-galaxy collection install $ANSIBLE_GALAXY_CLI_COLLECTION_OPTS -r requirements.yml --collections-path "/usr/share/ansible/collections"
# Configure ansible-runner
RUN ansible-playbook ansible_runner_setup.yml
# Copy helmfile
COPY --from=helmfile /usr/local/bin/helmfile /usr/local/bin/helmfile
ENV USER runner
ENV FOLDER /home/runner
RUN /usr/sbin/groupadd $USER && \
/usr/sbin/useradd $USER -m -d $FOLDER -g $USER -s /bin/bash && \
echo $USER 'ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL' >> /etc/sudoers
RUN for dir in \
/runner \
/var/lib/letsencrypt \
/etc/letsencrypt \
/var/log/letsencrypt ; \
do mkdir -p $dir ; chown $USER:$USER $dir; chmod 775 $dir ; done
USER $USER
RUN echo "export GPG_TTY=\$(tty)" >> /home/runner/.bashrc
WORKDIR /runner
The image automatically installs:
- Ansible PIP packages:
ansible-coreandansible-runner - Ansible requirements: ansible collections and roles in
build/requirements.yml - Certbot PIP package:
certbot - Additional PIP packages in
build/requirements.txt(packages needed by Ansible modules or cerbot plugins) helmandkubectlbinaries installation using Ansible (build/ansible_runner_config.yaml)helmfilebinary. Helmfile is used during bootstrap process to orchestrate the deployment of some HelmCharts.
Docker-compose file
docker-compose.yml
services:
# Ansible-runner
ansible-runner:
image: ansible-runner
build:
context: .
command: tail -f /dev/null
container_name: ansible-runner
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- ./../ansible:/runner
- ./../kubernetes:/kubernetes
- ./../metal/x86/pxe-files:/metal/x86/pxe-files
- ./runner/.gnupg:/home/runner/.gnupg
- ./runner/.vault:/home/runner/.vault
- ./runner/.secrets:/home/runner/.secrets
- ./runner/scripts:/home/runner/scripts
- ./runner/.ssh:/home/runner/.ssh
- ./runner/.kube:/home/runner/.kube
- ./certbot/log:/var/log/letsencrypt
- ./certbot/config:/etc/letsencrypt
- ./certbot/work:/var/lib/letsencrypt
This docker-compose file build and start ansible-runner docker container and mount several host’s directories including ansible’s project structure. The container is always running (command is tail -f /dev/null), so commands using it can be executed using docker exec and it is not needed to recreate a new container (docker run) every time a command need to be executed
ansible-runner container can be started with the command:
docker compose up --detach
Any command, including ansible’s commands, can be executed using the container
docker exec -it ansible-runner <command>
A shell session can be opened using the same container with:
docker exec -it ansible-runner /bin/bash
Ansible Configuration
Ansible source code is structured following typical directory layout:
📁 ansible
├── 📁 host_vars
├── 📁 group_vars
├── 📁 vars
├── 📁 tasks
├── 📁 templates
├── 📁 roles
├── ansible.cfg
├── inventory.yml
├── playbook1.yml
├── playbook2.yml
Where:
host_varsandgroup_varscontains Ansible variables belonging to hosts and groupsvarscontains Ansible’s variables files used by playbookstaskscontains Ansible’s tasks files used by playbookstemplatescontains Jinja2’s templates used by playbooksrolescontains Ansible’s roles
Ansible configuration is in ansible.cfg file containing paths to roles, collections and inventory file:
ansible.cfg
[defaults]
# Inventory file location
inventory = ./inventory.yml
# Ansible execution threads
forks = 5
# Paths to search for roles in, colon separated
roles_path = ./roles:/usr/share/ansible/roles
# Path for collections
collections_path = ./collections:/usr/share/ansible/collections
# Disable SSH key host checking
host_key_checking = false
Important:
All ansible commands (ansible, ansible-galaxy, ansible-playbook, ansible-vault) need to be executed within [/ansible] directory, so the configuration file /ansible/ansible.cfg can be used. Playbooks are configured to be launched from this directory.
Encrypting secrets/key variables
Ansible Vault can be used to encrypt secrets and keys stored in ansible variables.
To simplify the encryption/decryption, all secrets/key/passwords variables are stored in a dedicated file, vars/vault.yml, so this file can be encrypted using Ansible Vault
vault.yml file is a Ansible vars file containing just a unique yaml variable, vault: a yaml dictionary containing all keys/passwords used by the different cluster components.
vault.yml sample file is like this:
---
vault:
# K3s secrets
k3s:
k3s_token: s1cret0
# ingress secrets
ingress:
admin:
user: admin
passwd: s1cret0
# Minio S3 secrets
minio:
root:
user: root
key: supers1cret0
restic:
user: restic
key: supers1cret0
....
The manual steps to encrypt passwords/keys used in all Playbooks is the following:
-
Edit content
var/vault.ymlfile specifying your own values for each of the key/password/secret specified. -
Encrypt file using ansible-vault
ansible-vault encrypt vault.ymlThe command ask for a ansible vault password to encrypt the file. After executing the command the file
vault.ymlis encrypted. Yaml content file is not readable.Note:
The file can be decrypted using the following command
ansible-vault decrypt vault.ymlThe password using during encryption need to be provided to decrypt the file After executing the command the file
vault.ymlis decrypted and show the content in plain text.File can be viewed decrypted without modifiying the file using the command
ansible-vault view vault.yaml
Automate Ansible Vault decryption with GPG
When using encrypted vault.yaml file all playbooks executed with ansible-playbook command need the argument --ask-vault-pass, so the password used to encrypt vault file can be provided when starting the playbook.
ansible-playbook playbook.yml --ask-vault-pass
Ansible vault password decryption can be automated using --vault-password-file parameter , instead of manually providing the password with each execution (--ask-vault-pass).
Ansible vault password file can contain the password in plain-text or a script able to obtain the password.
vault-password-file location can be added to ansible.cfg file, so it is not needed to pass as parameter each time ansible-playbook command is executed
Linux GPG will be used to encrypt Ansible Vault passphrase and automatically obtain the vault password using a vault-password-file script.
-
GnuPG Installation and configuration
In Linux GPG encryption can be used to encrypt/decrypt passwords and tokens data using a GPG key-pair
GnuPG package has to be installed and a GPG key pair need to be created for encrytion/decryption
-
Step 1. Install GnuPG packet
sudo apt install gnupgCheck if it is installed
gpg --help -
Step 2. Generating Your GPG Key Pair
GPG key-pair consist on a public and private key used for encrypt/decrypt
gpg --gen-keyThe process requires to provide a name, email-address and user-id which identify the recipient
The output of the command is like this:
gpg (GnuPG) 2.2.4; Copyright (C) 2017 Free Software Foundation, Inc. This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it. There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law. Note: Use "gpg --full-generate-key" for a full featured key generation dialog. GnuPG needs to construct a user ID to identify your key. Real name: Ricardo Email address: ricsanfre@gmail.com You selected this USER-ID: "Ricardo <ricsanfre@gmail.com>" Change (N)ame, (E)mail, or (O)kay/(Q)uit? O We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number generator a better chance to gain enough entropy. We need to generate a lot of random bytes. It is a good idea to perform some other action (type on the keyboard, move the mouse, utilize the disks) during the prime generation; this gives the random number generator a better chance to gain enough entropy. gpg: /home/ansible/.gnupg/trustdb.gpg: trustdb created gpg: key D59E854B5DD93199 marked as ultimately trusted gpg: directory '/home/ansible/.gnupg/openpgp-revocs.d' created gpg: revocation certificate stored as '/home/ansible/.gnupg/openpgp-revocs.d/A4745167B84C8C9A227DC898D59E854B5DD93199.rev' public and secret key created and signed. pub rsa3072 2021-08-13 [SC] [expires: 2023-08-13] A4745167B84C8C9A227DC898D59E854B5DD93199 uid Ricardo <ricsanfre@gmail.com> sub rsa3072 2021-08-13 [E] [expires: 2023-08-13]During the generation process you will be prompted to provide a passphrase.
This passphrase is needed to decryp
-
-
Generate Vault password and store it in GPG
Generate the password to be used in ansible-vault encrypt/decrypt process and ecrypt it in using GPG
-
Step 1. Install pwgen packet
sudo apt install pwgen -
Step 2: Generate Vault password and encrypt it using GPG. Store the result as a file in $HOME/.vault
mkdir -p $HOME/.vault pwgen -n 71 -C | head -n1 | gpg --armor --recipient <recipient> -e -o $HOME/.vault/vault_passphrase.gpgwhere
<recipient>must be the email address configured during GPG key creation. -
Step 3: Generate a script
vault_pass.sh#!/bin/sh gpg --batch --use-agent --decrypt $HOME/.vault/vault_passphrase.gpg -
Step 4: Modify
ansible.cfgfile, so you can omit the--vault-password-fileargument.[defaults] vault_password_file=vault_pass.sh
Note: If this repository is clone steps 3 and 4 are not needed since the files are already there.
-
-
Encrypt vautl.yaml file using ansible-vault and GPG password
ansible-vault encrypt vault.yamlThis time only your GPG key passphrase will be asked to automatically encrypt/decrypt the file
Installing Ansible Development Environment
For having a complete Ansible development enviroment the following environment setup is recommended:
- Docker: Docker is used by Molecule, Ansible’s testing tool, for building the testing environment, so it is needed to have a Docker installation on the Control Node for developing and testing the Ansible Playbooks/Roles.
- Vagrant and KVM: Used by Molecule, to automate the testing of some of the roles that requires a VM and not a docker image (example: Storage roles)
- Ansible and Molecule packages running in a Virtual Python environment
Installing KVM and Vagrant
In order to automate the testing of some of the roles that requires a VM and not a docker image (example: Storage roles), KVM and Vagrant will be installed
Enable nested virtualization within the VM
Need to be changed with the command line. Not supported in GUI
vboxmanage modifyvm <pimaster-VM> --nested-hw-virt on
KVM installation in Ubuntu 20.04
-
Step 1. Install KVM packages and its dependencies
sudo apt install qemu qemu-kvm libvirt-clients libvirt-daemon-system virtinst bridge-utils -
Step 2. Enable on boot and start libvirtd service (If it is not enabled already):
sudo systemctl enable libvirtd sudo systemctl start libvirtd -
Step 3. Add the user to libvirt group
sudo usermod -a -G libvirtd $USER
Vagrant installation in Ubuntu 20.04
-
Step 1. Add hashicorp apt repository
curl -fsSL https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com/gpg | sudo apt-key add - sudo apt-add-repository "deb [arch=amd64] https://apt.releases.hashicorp.com $(lsb_release -cs) main" sudo apt-get update -
Step 2. Install vagrant
sudo apt install vagrant
Install vagrant-libvirt plugin in Linux
In order to run Vagrant virtual machines on KVM, you need to install the vagrant-libvirt plugin. This plugin adds the Libvirt provider to Vagrant and allows Vagrant to control and provision machines via Libvirt
-
Step 1. Install dependencies
sudo apt install build-essential qemu libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients libxslt-dev libxml2-dev libvirt-dev zlib1g-dev ruby-dev ruby-libvirt ebtables dnsmasq-base libguestfs-tools -
Step 2. Install vagrant-libvirt plugin:
vagrant plugin install vagrant-libvirt -
Step 3. Install mutate plugin which converts vagrant boxes to work with different providers.
vagrant plugin install vagrant-mutate
Installing Ansible and Molecule testing environment
Ansible can be installed in Ubuntu 20.04 using official package from the ansible repository ‘sudo apt install ansible’ will install an old ansible verion.
Ansible Molecule is not available as official package, so pip is the only alternative Instead, install latest version for python3 with python package manager pip.
Python Ansible and Molecule packages and its dependencies installed using Pip might conflict with python3 packages included in the Ubuntu official release, so packages installation should be done using non-root user (local user packages installation) or within a python virtual environment.
Installation of the whole Ansible environment can be done using a python virtual environment.
-
Step 1. Install python Virtual Env and Pip3 package
sudo apt-get install python3-venv python3-pip -
Step 2. Create Virtual Env for Ansible
python3 -m venv ansible -
Step 3. Activate Virtual Environment
source ansible/bin/activateNote: For deactivating the Virtual environment execute command
deactivate -
Step 4. Upgrade setuptools and pip packages
pip3 install --upgrade pip setuptools -
Step 5. Install ansible
pip3 install ansible -
Step 6. Install yamllint, ansible-lint and jmespath (required by ansible json filters)
pip3 install yamllint ansible-lint jmespath -
Step 7. Install Docker python driver and molecule packages:
pip3 install molecule molecule-plugins[docker] docker -
Step 8. Install molecule vagrant driver
pip3 install molecule-vagrant python-vagrant
Create public/private SSH key for remote connection
Authentication using SSH keys will be the only mechanism available to login to any server in the Pi Cluster.
In order to improve security, default UNIX user, ubuntu, created by cloud images will be disabled. A new unix user, ricsanfre, will be created in all servers with root privileges (sudo permissions). This user will be used to connect to the servers from my home laptop and to automate configuration activities using Ansible (used as ansible_remote_user when connecting).
ssh private/public keys will be created for the different purposes (admin SSH connection and Ansible connection). Public ssh keys can be added to the UNIX user created in all servers as ssh-authorized-keys to enable passwordless SSH connection.
Default user in cluster nodes and its authorized SSH public keys will be added to cloud-init configuration (user-data), when installing Ubuntu OS.
SSH keys generation
For generating SSH private/public key in Windows, Putty Key Generator can be used:
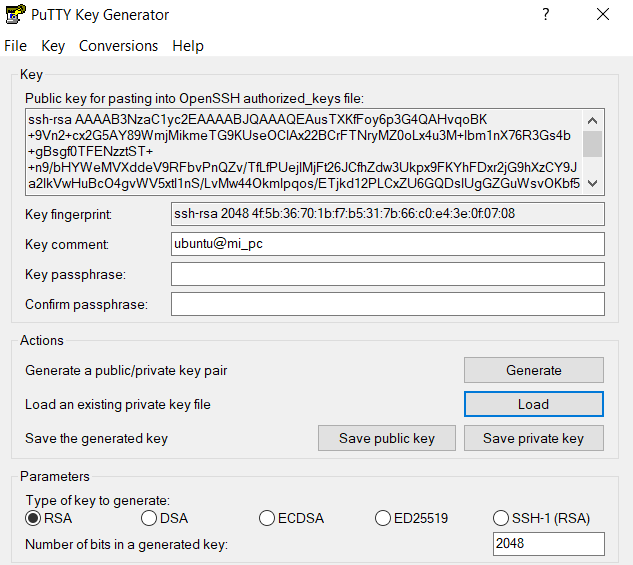
Public-key string will be used as ssh_authorized_keys of the privileged user (i.e.: ricsanfre) in cloud-init user-data
For generating ansible SSH keys in Linux server execute command:
ssh-keygen
In directory $HOME/.ssh/ public and private key files can be found for the user
id_rsa contains the private key and id_rsa.pub contains the public key.
Content of the id_rsa.pub file has to be used as ssh_authorized_keys of UNIX user created in cloud-init user-data
cat id_rsa.pub
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDsVSvxBitgaOiqeX4foCfhIe4yZj+OOaWP+wFuoUOBCZMWQ3cW188nSyXhXKfwYK50oo44O6UVEb2GZiU9bLOoy1fjfiGMOnmp3AUVG+e6Vh5aXOeLCEKKxV3I8LjMXr4ack6vtOqOVFBGFSN0ThaRTZwKpoxQ+pEzh+Q4cMJTXBHXYH0eP7WEuQlPIM/hmhGa4kIw/A92Rm0ZlF2H6L2QzxdLV/2LmnLAkt9C+6tH62hepcMCIQFPvHVUqj93hpmNm9MQI4hM7uK5qyH8wGi3nmPuX311km3hkd5O6XT5KNZq9Nk1HTC2GHqYzwha/cAka5pRUfZmWkJrEuV3sNAl ansible@pimaster