Load Balancer (Metal LB)
Important: Deprecated Technology in PiCluster project
Kubernetes CNI solution for the cluster has been migrated to Cilium in release 1.9. Metal LB load balancer has been replaced by Cilium’s LB-IPAM capability.
Metal-LB technology has been deprecated and this documentation is not updated anymore.
Reasons behind this decission in PiCluster 1.9 release announcement.
See how to configure Cilium Load Balancer in: “Cilium (Kubernetes CNI)”.
Instead of using the embeded service load balancer that only comes with K3S, kippler-lb, a more generic kubernetes load balancer like Metal LB will be used. This load balancer can be used with almost any distribution of kubernetes.
In order to use Metal LB, K3S embedded Klipper Load Balancer must be disabled: K3s server installation option --disable servicelb.
After K3S fresh installation disabling embedded service load balanced, the following pods and services are started by default:
kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system metrics-server-86cbb8457f-k52mz 1/1 Running 0 7m45s
kube-system local-path-provisioner-5ff76fc89d-qzfpp 1/1 Running 0 7m45s
kube-system coredns-7448499f4d-wk4sd 1/1 Running 0 7m45s
kube-system helm-install-traefik-crd-5r72x 0/1 Completed 0 7m46s
kube-system helm-install-traefik-86kpb 0/1 Completed 2 7m46s
kube-system traefik-97b44b794-vtj7x 1/1 Running 0 5m24s
kubectl get services --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.43.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 8m32s
kube-system kube-dns ClusterIP 10.43.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 8m29s
kube-system metrics-server ClusterIP 10.43.169.140 <none> 443/TCP 8m28s
kube-system traefik LoadBalancer 10.43.50.56 <pending> 80:30582/TCP,443:30123/TCP 5m53s
Why Metal LB
Kubernetes does not offer an implementation of network load balancers (Services of type LoadBalancer) for bare-metal clusters. The implementations of network load balancers that Kubernetes does ship with are all glue code that calls out to various IaaS platforms (GCP, AWS, Azure…).
In bare-metal kubernetes clusters, like the one I am building, “LoadBalancer” services will remain in the “pending” state indefinitely when created. See in previous output of kubectl get services command how traefik LoadBAlancer service “External IP” is “pending”.
For Bare-metal cluster, only two options remain available for managing incoming traffic to the cluster: “NodePort” and “externalIPs” services. Both of these options have significant downsides for production use, which makes bare-metal clusters second-class citizens in the Kubernetes ecosystem.
MetalLB provides a network load balacer that can be integrated with standard network equipment, so that external services on bare-metal clusters can be accesible using a pool of “external” ip addresses.
How Metal LB works
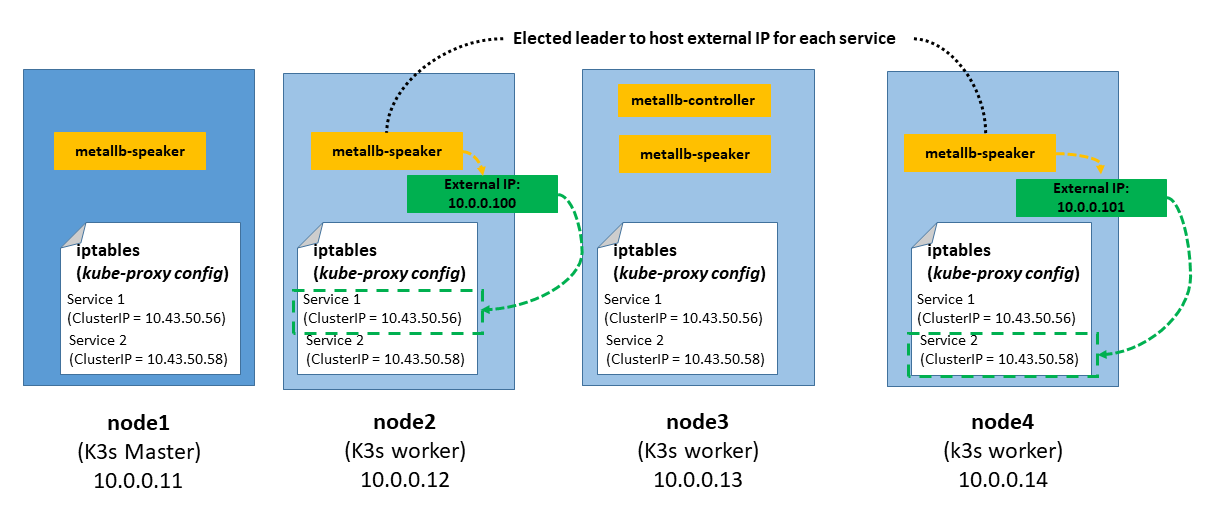
MetalLB can work in two modes, BGP and Layer 2. The major advantage of the layer 2 mode is its universality: it will work on any Ethernet network. In BGP mode specific routers are needed to deploy the solution.
In layer 2 mode, one node assumes the responsibility of advertising a particular kuberentes service (LoadBalance type) to the local network, this is call the leader node. From the network’s perspective, it simply looks like that node has multiple IP addresses assigned to its network interface and it just responds to ARP requests for IPv4 services, and NDP requests for IPv6.
When configuring MetalLB in layer 2 mode, all traffic for a service IP goes to the leader node. From there, kube-proxy spreads the traffic to all the service’s pods. Thus MetalLB layer 2 really does not implement a load balancer. Rather, it implements a failover mechanism so that a different node can take over should the current leader node fail for some reason.
MetalLB consists of two different pods:
- Controller: resposible for handling IP address assigments from a configured Pool.
- Speaker: DaemonSet pod running on each worker node, resposible for announcing the allocated IPs.
How to use
After Metal-LB is installed and configured, to expose a Kubernetes Service externally, simply it has to be created with spec.type set to LoadBalancer, and MetalLB will do the rest.
Requesting Specific IPs
Metal-LB supports custom metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs annotation that can be set in the Service to use a specific IP of Metal-LB pool.
if Metal-LB does not own the requested address, or if the address is already in use by another service, assignment will fail and MetalLB will log a warning event visible in kubectl describe service <service name>.
The annotation also supports a comma separated list of IPs to be used in case of Dual Stack services.
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
annotations:
metallb.universe.tf/loadBalancerIPs: 192.168.1.44
See details in Metal-LB usage doc
Install Metal Load Balancer
Installation using Helm (Release 3):
-
Step 1: Add the Metal LB Helm repository:
helm repo add metallb https://metallb.github.io/metallb -
Step 2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update -
Step 3: Create namespace
kubectl create namespace metallb -
Step 4: Install Metallb in the
metallbnamespace.helm install metallb metallb/metallb --namespace metallb -
Step 5: Confirm that the deployment succeeded, run:
kubectl -n metallb get pod -
Step 6: Configure IP addess pool and the announcement method (L2 configuration)
Create the following manifest file:
metallb-config.yaml--- # Metallb address pool apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1 kind: IPAddressPool metadata: name: picluster-pool namespace: metallb spec: addresses: - 10.0.0.100-10.0.0.200 --- # L2 configuration apiVersion: metallb.io/v1beta1 kind: L2Advertisement metadata: name: example namespace: metallb spec: ipAddressPools: - picluster-poolApply the manifest file
kubectl apply -f metallb-config.yamlAfter a while, metallb is deployed and traefik LoadBalancer service gets its externa-ip from the configured pool and is accessible from outside the cluster
kubectl get services --all-namespaces NAMESPACE NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE default kubernetes ClusterIP 10.43.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 63m kube-system kube-dns ClusterIP 10.43.0.10 <none> 53/UDP,53/TCP,9153/TCP 63m kube-system metrics-server ClusterIP 10.43.169.140 <none> 443/TCP 63m kube-system traefik LoadBalancer 10.43.50.56 10.0.0.100 80:30582/TCP,443:30123/TCP 60m