Log Aggregation (Loki)
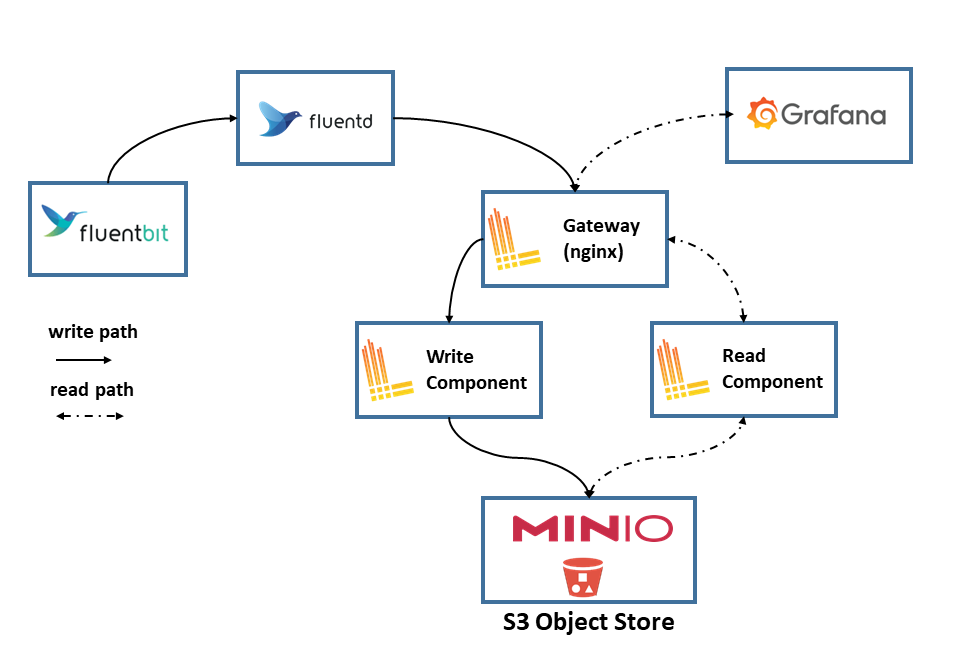
Loki architecture
Loki architecture is displayed in the following picture (source: Grafana documentation):
All Loki components are included within a single binary (docker image) that supports three different deployments modes where the above components can be started in different PODs
-
Monolithic
In this mode, all Loki components are running in a single process (container).
-
Simple scalable mode
In this deployment, Loki is deployed in HA, deploying replicas of write and read nodes (processes)
- Write nodes: supporting write path. Distributor and Ingestor components, responsible to store logs and indexes in the back-end storage (Minio S3 storage)
- Read nodes: supporting read path. Ruler, Querier and Frontend Querier components, responsible to answer to log queries.
- Backend nodes: loki backend services Compactor, Index gateways and Query scheduler – Ruler
- Gateway node: a load balancer in front of Loki (nginx based), which directs
/loki/api/v1/pushtraffic to the write nodes. All other requests go to the read nodes. Traffic should be sent in a round robin fashion.
-
Microservices In this deployment each individual Loki component can be started in an independent process (container).
Further details in Loki architecture documentation: Loki components and deployment modes
Loki will be installed using Simple scalable deployment mode using as S3 Object Storage Server (Minio) as backend.
Configure S3 Minio Server
Minio Storage server is used as Loki long-term data storage.
Grafana Loki needs to store two different types of data: chunks and indexes. Both of them can be stored in S3 server.
Note:
Loki helm chart is able to install this Minio service as a subchart, but its installation will be disabled and Minio Storage Service already deployed in the cluster will be used as Loki’s backend.
As part of Minio Storage Service installation, loki’s S3 bucket, policy and user is already configured. See documentation: Minio S3 Object Storage Service.
Create Minio user and bucket
Use Minio’s mc command to create loki bucket and user
mc mb <minio_alias>/k3s-loki
mc admin user add <minio_alias> loki <user_password>
Note:
As the Loki’s documentation said, when using S3 as object storage, the following permissions are needed:
- s3:ListBucket
- s3:PutObject
- s3:GetObject
- s3:DeleteObject (if running the Single Store (boltdb-shipper) compactor)
Over the resources: arn:aws:s3:::
Apply policy to user loki so it has the proper persmissions on k3s-loki bucket.
mc admin policy add <minio_alias> loki user_policy.json
Where user_policy.json, contains the following AWS access policies definition:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:DeleteObject",
"s3:GetObject",
"s3:ListBucket",
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::k3s-loki",
"arn:aws:s3:::k3s-loki/*"
]
}
]
}
See further details in Loki-Storage documentation
Loki installation
Installation from helm chart. There are two alternatives:
-
Loki-stack helm chart. With this helm chart the complete PLG stack can be installed.
This helm chart will not be used because we are only interested in deploying Loki component. Promtail will not be used and Grafana will be deployed as part of kube-prometheus-stack.
-
Loki-helm chart v3.x. Used for Monolithic and Simple scalable deployment modes](https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/fundamentals/architecture/deployment-modes/#simple-scalable-deployment-mode).
This is the helm chart we will use to deploy Loki in HA (simple scalable deployment mode).
- Step 1: Add the Grafana repository:
helm repo add grafana https://grafana.github.io/helm-charts - Step2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update - Step 3: Create namespace
kubectl create namespace loki -
Step 4: Create file
loki-values.yml# Setting simple scalable deployment mode deploymentMode: SimpleScalable loki: # Disable multi-tenant support auth_enabled: false # S3 backend storage configuration storage: bucketNames: chunks: <minio_loki_bucket> ruler: <minio_loki_bucket> type: s3 s3: endpoint: <minio_endpoint> region: <minio_site_region> secretAccessKey: <minio_loki_key> accessKeyId: <minio_loki_user> s3ForcePathStyle: true insecure: false http_config: idle_conn_timeout: 90s response_header_timeout: 0s insecure_skip_verify: false # Storage Schema schemaConfig: configs: - from: 2024-04-01 store: tsdb index: prefix: loki_index_ period: 24h object_store: s3 schema: v13 # Configuration for the write write: # Number of replicas for the write replicas: 3 persistence: # -- Size of persistent disk size: 10Gi # -- Storage class to be used. storageClass: longhorn # Configuration for the read read: # Number of replicas for the read replicas: 3 persistence: # -- Size of persistent disk size: 10Gi # -- Storage class to be used. storageClass: longhorn # Configuration for the backend backend: # Number of replicas for the backend replicas: 3 persistence: # -- Size of persistent disk size: 10Gi # -- Storage class to be used. storageClass: longhorn # Configuration for the gateway gateway: # -- Specifies whether the gateway should be enabled enabled: true # -- Number of replicas for the gateway replicas: 1 # Disable mino installation minio: enabled: false # Disable self-monitoring monitoring: selfMonitoring: enabled: false grafanaAgent: installOperator: false lokiCanary: enabled: false # Disable helm-test test: enabled: falseThis configuration:
-
Set simple scalable deployment mode (
deploymentMode: SimpleScalable) -
Disable multi-tenant support (
auth_enabled: false) so it is not needed to provide org_id in HTTP headers. -
Enable S3 as storage backend, providing Minio credentials and bucket. (
loki.storage). -
Configure TSDB as storage schema (
loki.schemaConfig). See Loki Storage Schema doc and TSDB Storage -
Configure three replicas for write (
write), read (read) and backend (backend)components and persistent volumes using Longhorn -
Enable one replica for gateway component (
gateway) -
Disable minio server installation (
minio.enabled) -
Disable self-monitoring (
monitoring.selfmonitoring) and helm-test validation (test.enabled)
-
- Step 5: Install Loki in
lokinamespacehelm install loki grafana/loki -f loki-values.yml --namespace loki - Step 6: Check status of Loki pods
kubectl get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=loki -n loki
GitOps installation
As an alternative, for GitOps deployments, instead of hardcoding minio credentials within Helm chart values, a external secret can be configured leveraging Loki’s capability of using environment variables in config file.
The following secret need to be created:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: loki-minio-secret
namespace: loki
type: Opaque
data:
MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID: < minio_loki_user | b64encode >
MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY: < minio_loki_key | b64encode >
And the following Helm values has to be provided:
loki:
# Disable multi-tenant support
auth_enabled: false
# S3 backend storage configuration
storage:
bucketNames:
chunks: k3s-loki
ruler: k3s-loki
type: s3
s3:
endpoint: s3.picluster.ricsanfre.com:9091
region: eu-west-1
secretAccessKey: ${MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY}
accessKeyId: ${MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID}
s3ForcePathStyle: true
insecure: false
http_config:
idle_conn_timeout: 90s
response_header_timeout: 0s
insecure_skip_verify: false
# Storage Schema
schemaConfig:
configs:
- from: 2024-04-01
store: tsdb
index:
prefix: loki_index_
period: 24h
object_store: s3
schema: v13
# Configuration for the write
write:
# Number of replicas for the write
replicas: 3
persistence:
# -- Size of persistent disk
size: 10Gi
# -- Storage class to be used.
storageClass: longhorn
# Enable environment variables in config file
# https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/configuration/#use-environment-variables-in-the-configuration
extraArgs:
- '-config.expand-env=true'
extraEnv:
- name: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: loki-minio-secret
key: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- name: MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: loki-minio-secret
key: MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
# Configuration for the read
read:
# Number of replicas for the read
replicas: 3
persistence:
# -- Size of persistent disk
size: 10Gi
# -- Storage class to be used.
storageClass: longhorn
# Enable environment variables in config file
# https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/configuration/#use-environment-variables-in-the-configuration
extraArgs:
- '-config.expand-env=true'
extraEnv:
- name: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: loki-minio-secret
key: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- name: MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: loki-minio-secret
key: MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
# Configuration for the backend
backend:
# Number of replicas for the backend
replicas: 3
persistence:
# -- Size of persistent disk
size: 10Gi
# -- Storage class to be used.
storageClass: longhorn
# Enable environment variables in config file
# https://grafana.com/docs/loki/latest/configuration/#use-environment-variables-in-the-configuration
extraArgs:
- '-config.expand-env=true'
extraEnv:
- name: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: loki-minio-secret
key: MINIO_ACCESS_KEY_ID
- name: MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: loki-minio-secret
key: MINIO_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY
# Configuration for the gateway
gateway:
# -- Specifies whether the gateway should be enabled
enabled: true
# -- Number of replicas for the gateway
replicas: 1
# Disable mino installation
minio:
enabled: false
# Disable self-monitoring
monitoring:
selfMonitoring:
enabled: false
grafanaAgent:
installOperator: false
lokiCanary:
enabled: false
# Disable helm-test
test:
enabled: false
Grafana Configuration
Loki need to be added to Grafana as DataSource
This can be done automatically when installing kube-prometheus-stack providing the following additional helm chart configuration:
grafana:
# Additional data source
additionalDataSources:
- name: Loki
type: loki
url: http://loki-read-headless.loki.svc.cluster.local
