DNS (CoreDNS and External-DNS)
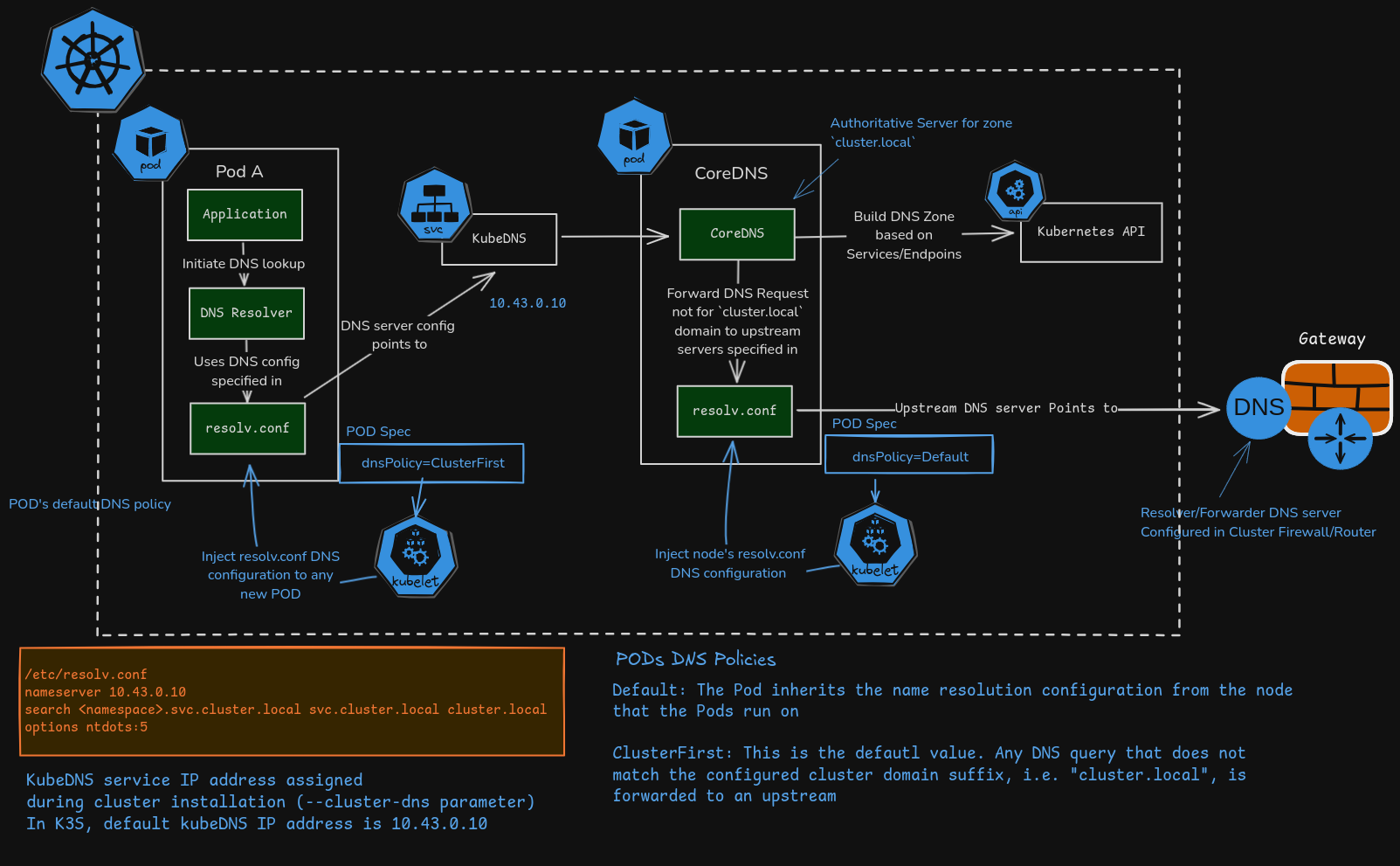
PODs within Kubernetes will use DNS service to discover Kubernetes services and external services. CoreDNS is the default Kubernetes DNS service that need to be deployed in the cluster.
Kubernetes DNS service provided by CoreDNS is complemented with ExternalDNS.
External DNS is used to synchronize exposed Kubernetes Services (LoadBalancer type services) and Ingresses with cluster authoritative DNS server, Bind9. So DNS records associated to exposed services can be automatically created and services can be accessed from out-side using their DNS names.
DNS kubernetes services will relay on DNS split horizon architecture deployed for the cluster. See details in Pi Cluster - DNS Architecture.
CoreDNS
Pods and kubernetes services are automatically discovered, using Kubernetes API, and assigned a DNS name within cluster-dns domain (default cluster.local) so they can be accessed by PODs running in the cluster.
CoreDNS also takes the role of Resolver/Forwarder DNS to resolve POD’s dns queries for any domain, using default DNS server configured at node level.
Installation
Using CoreDNS Helm Chart
-
Step 1: Add Git repo
helm repo add coredns https://coredns.github.io/helm -
Step 2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update -
Step 3. Create helm values file
core-values.yamlreplicaCount: 3 k8sAppLabelOverride: kube-dns serviceAccount: create: true service: name: kube-dns clusterIP: 10.43.0.10 # Default zone is what Kubernetes recommends: # https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/dns-custom-nameservers/#coredns-configmap-options servers: - zones: - zone: . port: 53 plugins: - name: errors # Serves a /health endpoint on :8080, required for livenessProbe - name: health configBlock: |- lameduck 5s # Serves a /ready endpoint on :8181, required for readinessProbe - name: ready # Required to query kubernetes API for data - name: kubernetes parameters: cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa configBlock: |- pods insecure fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa ttl 30 # Serves a /metrics endpoint on :9153, required for serviceMonitor - name: prometheus parameters: 0.0.0.0:9153 - name: forward parameters: . /etc/resolv.conf - name: cache parameters: 30 - name: loop - name: reload - name: loadbalanceWith this configuration 3 replicas of coreDNS POD will be created (
replicaCount).kube-dns(service.name) service will be created with IP addess (service.clusterIp) used during installation of K3s control plane(--cluster-dns) parameter, set by default by K3s to10.43.0.10.CoreDNS configuration (
servers) is providing the same options for Corefile recommended by Kubernetes. See details of these default options in Customized DNS options- CoreDNS ConfigMap options -
Step 4. Install CoreDNS in kube-system namespace
helm install coredns coredns/coredns --namespace=kube-system -f core-dns-values.yaml -
Step 5. Confirm that the deployment succeeded, run:
kubectl get pod -n kube-system
ExternalDNS
ExternalDNS synchronizes exposed Kubernetes Services and Ingresses with DNS providers.
ExternalDNS allows you to control DNS records dynamically via Kubernetes resources in a DNS provider-agnostic way.
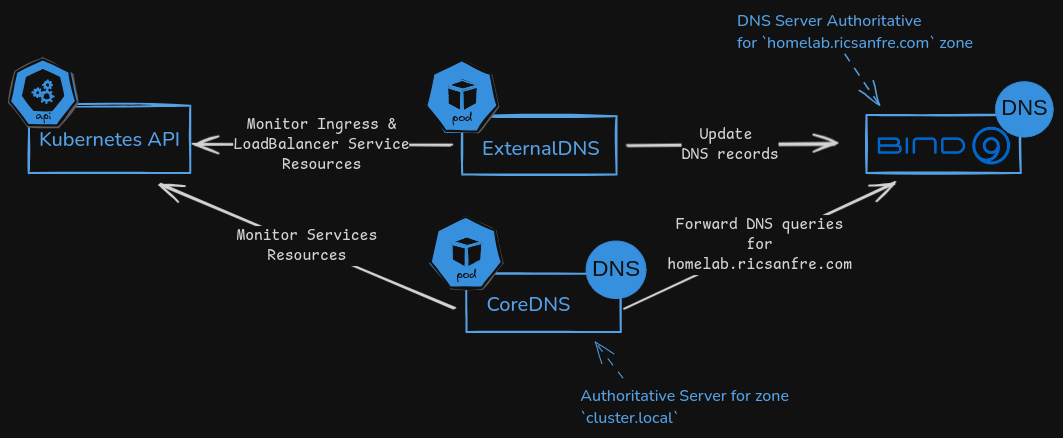
ExternalDNS makes Kubernetes resources discoverable via public DNS servers. Like CoreDNS, it retrieves a list of resources (Services, Ingresses, etc.) from the Kubernetes API to determine a desired list of DNS records. Unlike CoreDNS, however, it’s not a DNS server itself, but merely configures other DNS providers.
Details on how to configure rfc2136 provider, used for integrating Bind9, can be found in External-DNS documentation- RFC2136 Provider.
Configuring rfc2136 provider (Bind9)
-
Step 1. Create TSIG shared key First a TSIG shared key can be created using
tsig-keygencommand:tsig-keygen -a hmac-sha512 externaldns-key > /etc/bind/keys/external-dns.key -
Step 2. Include shared key in
namedconfigurationUpdate
named.conf.optionsfile with the following// The following keys are used for dynamic DNS updates include "/etc/bind/keys/external-dns.key"; -
Step 3. Configure zone to accept dynamic updates
Dynamic updates from external-dns is allowed including
update-policyandallow-transferclauses in thezonestatement.Update
named.conf.localzone "homelab.ricsanfre.com" { type primary; file "/var/lib/bind/db.homelab.ricsanfre.com"; allow-transfer { key "externaldns-key"; }; update-policy { grant extenaldns-key zonesub any; }; }; -
Step 4. Reload or restart bind9
sudo systemctl restart bind9
Installation
-
Step 1. Add Helm repository
helm repo add external-dns https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/external-dns/ -
Step 2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update -
Step 3: Create namespace
kubectl create namespace external-dns -
Step 4. Store TSIG secret into a Kubernetes secret
Create manifest
external-dns-bind-secret.yamlapiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: external-dns-bind9-secret namespace: external-dns data: ddns-key: <base64 encode of the tsig key>Apply manifest file:
kubectl apply -f external-dns-bind-secret.yaml -
Step 5. Create helm values file
external-dns-values.yamlprovider: name: rfc2136 env: - name: EXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_HOST value: "10.0.0.11" - name: EXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_PORT value: "53" - name: EXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_ZONE value: homelab.ricsanfre.com - name: EXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_TSIG_AXFR value: "true" - name: EXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_TSIG_KEYNAME value: externaldns-key - name: EXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_TSIG_SECRET_ALG value: hmac-sha512 - name: EXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_TSIG_SECRET valueFrom: secretKeyRef: name: external-dns-bind9-secret key: ddns-key policy: sync registry: txt txtOwnerId: k8s txtPrefix: external-dns- sources: - crd - service - ingress domainFilters: - homelab.ricsanfre.com serviceMonitor: enabled: trueWith this configuration External-DNS will listen to Ingress, Services, Istio-Gateway and external-dns specific DNSEndpoint Resources (
sources) containing references to hostnames in domainhomelab.ricsanfre.com(domainFilter), and it will create the corresponding DNS records in the DNS server specified byEXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_HOSTenvironement variable using the TGSIG key speficied byEXTERNAL_DNS_RFC2136_TSIG_*environment variables.It also enables the Prometheus
serviceMonitor.enabledImportant:
Environment variables external-dns supports all arguments as environment variables adding the prefix “EXTERNAL_DNS_” and uppercasing the parameter name, converting all hyphen into underscore so
rfc2136-tsig-secret, becomes EXTERNAL_DNS_RFF1236_TSIG_SECRET -
Step 6. Install external-dns into
external-dnsnamespacehelm install external-dns external-dns/external-dns -n external-dns -f external-dns-values.yaml -
Step 7: Confirm that the deployment succeeded, run:
kubectl -n external-dns get pod
Use external-dns
To use external-dns add an ingress or a LoadBalancer service with a host that is part of the domain-filter
For example the following wll add A records to the DNS:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/hostname: svc.homelab.ricsanfre.com
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
selector:
app: nginx
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: my-ingress
spec:
rules:
- host: ingress.homelab.ricsanfre.com
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: my-service
servicePort: 8000
Services of type “LoadBalancer” need to be annotated with external-dns-aplpha.kubernetes.io/hostname
Ingress resources does not need to be annotated. If the host is part of domain-filter it will be added automatically.
Also new DNS records can be created using external-dns specific CRD (DNSEndpoint)
apiVersion: externaldns.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: DNSEndpoint
metadata:
name: examplednsrecord
spec:
endpoints:
- dnsName: foo.homelab.ricsanfre.com
recordTTL: 180
recordType: A
targets:
- 10.0.0.216