GitOps (FluxCD)
What is Flux
FluxCD is a tool for providing Continuous Delivery workflows on Kubernetes using GitOps principles. It enables the managing and automating the deployment and configuration of applications and infrastructure within a Kubernetes cluster, promoting a declarative and version-controlled approach to operations.
Flux Architecture
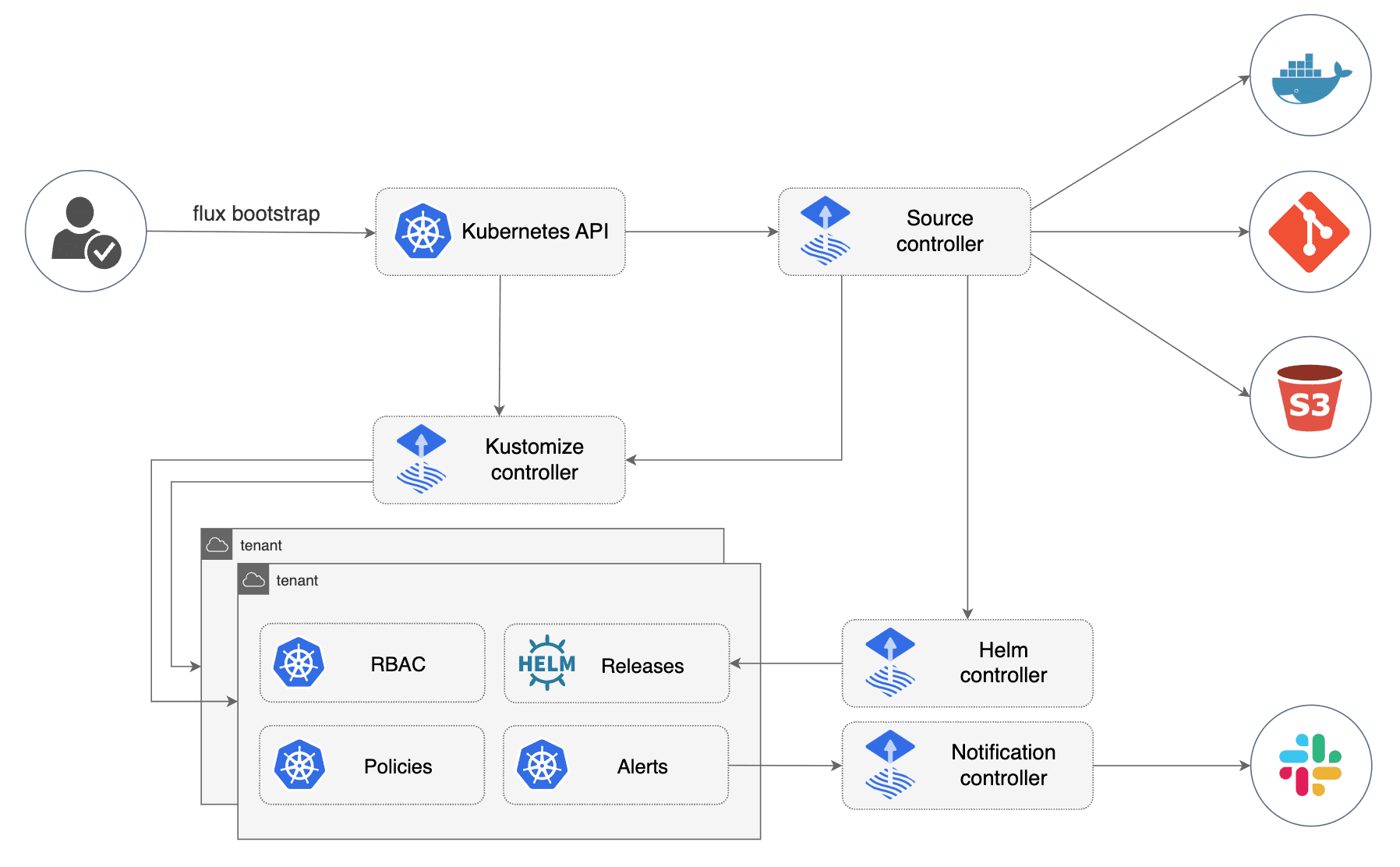
Flux is composed of a set of Kubernetes Controllers and Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs). Applications to be deployed in the Kubernetes cluster can be defined declarative using a set of Kubernetes manifest files using those CRDs and store them in Git repository. Flux Controllers will take care of synchronize (reconcile) the manifest files stored in Git repository with the state in Kubernetes cluster.
With Flux manifest files storing can be synchronize from different Sources (Git Repository, OCI Repository, Helm Repository or S3 Bucket)
- Source Controller in charge of reconcile different Sources
- Sources are defined declarative using specific Flux CRDs:
GitRepository
Kubernetes applications, to be deployed in Flux, can be defined using plain manifest kubernetes files (not packaged) or kubernetes applications packaged using: Kustomize and/or Helm
- Helm Controller in charge of reconcile Helm applications
- Kustomize Controller in charge of reconcile applications defined in plain manifest files or packaged with Kustomize.
- Helm and Kustomize applications are declared using specific Flux CRDs:
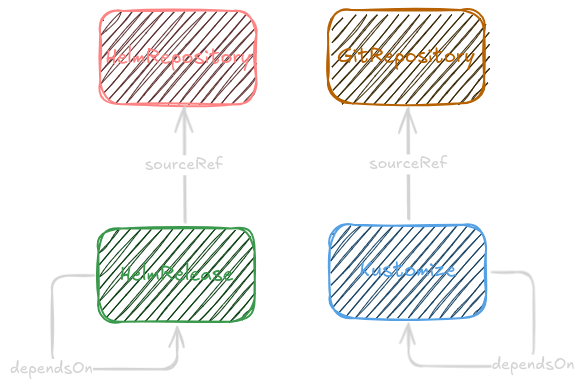
KustomizationandHelmRealease
sequenceDiagram
participant HelmRepository
participant HelmController
participant Kubernetes API
alt Check & Update
HelmController->>HelmRepository: Check new version
HelmRepository->>HelmController: Download if new version
end
alt Rendering & Deployment
HelmController->>HelmController: Render chart
HelmController->>Kubernetes API: Apply manifests
end
Flux CRDs
GitRepository
Flux GitRepository reference doc
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: GitRepository
metadata:
name: myRepo
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 30m
ref:
branch: master
secretRef:
name: mySecret
url: https://github.com/ricsanfre/flux-cd.git
Where:
spec.url: HTTP/S or SSH address of the Git repository.spec.ref.branch: Git repository branchspec.interval: it specifies the interval at which the Git repository must synchronizedspec.secretRef.name: Optional field. Secret in the same namespace as the GitRepository, containing authentication credentials for the Git repository (only needed for private repositories)
Secret
To authenticate towards a Git repository over HTTPS using basic access authentication (using a username and password (GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT)), the referenced Secret is expected to contain .data.username and .data.password values.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: basic-access-auth
type: Opaque
data:
username: <BASE64>
password: <BASE64>
Where:
.data.username: is the user used to access the repo.data.password: is the GitHub PAT used to access the repo
Secret can also be generated automatically using flux cli command.
flux create secret git flux-system \
--url=https://github.com/ricsanfre/flux-cd.git \
--username=git \
--password=password
See command reference: https://fluxcd.io/flux/cmd/flux_create_secret_git/
Note: See details about Github HTTP authentication in Git documentation - Authenticating to the REST API
Tip:
flux bootstrap git command automatically creates the secret containing the following data
username = flux
password = <github_pat>
HelmRepository
Flux HelmRepository reference doc
---
apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: HelmRepository
metadata:
name: coredns
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 5m0s
url: https://coredns.github.io/helm
Where:
spec.url: is the helm repo urispec.interval: It is a an optional field that specifies the interval which the Helm repository index must be consulted at. When not set, the default value is1m.
Kustomization
Flux Kustomization reference doc
Kustomization CRD, defines a pipeline for fetching, decrypting, building, validating and applying Kustomize overlays or plain Kubernetes manifests
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: myapp
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 30m
targetNamespace: mynamespace
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: myRepo
dependsOn:
- name: external-secrets-config
- name: longhorn-app
path: ./kubernetes/platform/minio/app/overlays/prod
prune: true
healthChecks:
- apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2
kind: HelmRelease
name: minio
namespace: minio
postBuild:
substituteFrom:
- kind: ConfigMap
name: cluster-settings
# Use this ConfigMap if it exists, but proceed if it doesn't.
optional: true
Where:
spec.sourceRef: Reference to the GitRepository where the application is locatedspec.path: Path within GitRepository where the kubernetes manifest files or the kustomize application is located.spec.targetNamespace: namespace where all the kuberentes manifest files will be deployed.spec.interval: specifies the interval at which the Kustomization runs a a server-side apply dry-run to detect and correct drift inside the cluster.spec.prune: It enables/disables garbage collection for a Kustomization. See details in Prune resources (Garbage Collection)spec.dependsOn: List of other Kustomization objects the application depends on. See details in Dependenciesspec.healthCheckslist of Kubernetes resources that are going to be checked to determine the rollout status of the Kustomization. See details in Health checks.spec.postBuild.substituteFrom: Use a specific ConfigMap/Secret to substitute variables defined in the Kubernetes manifest files. See details in Flux Kustomization Templating
Prune resources (Garbage Collection)
Garbage collection means that the Kubernetes objects that were previously applied on the cluster but are missing from the current source revision, are removed from the cluster automatically.
Garbage collection is also performed when a Kustomization object is deleted, triggering a removal of all Kubernetes objects previously applied on the cluster. The removal of the Kubernetes objects is done in the background, i.e. it doesn’t block the reconciliation of the Kustomization.
To enable garbage collection for a Kustomization, spec.prune has to be set to true.
Pruning for certain resources can be disabled by either labelling or annotating them with:
kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/prune: disabled
Health checks
Each Kustomization resource can be configured to perform health checks on the reconciled resources. This will be used to determine the rollout status of the deployed workloads. In addition it can check the ready status of custom resources.
To enable health checking, set spec.wait to true (default value is false). This will enable the health check for all reconciled resources. Also spec.timeout (default 5 minutes) can be adjusted to configure a timeout for the health check operation
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: my-kustomization
spec:
interval: 30m
targetNamespace: target-namespace
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system
path: ./kubernetes/platform/application/overlays/prod
prune: true
wait: true
timeout: 10m
retryInterval: 2m
With this configuration Kustomization controller will check the health of all reconciled resources (wait: true) and it will wait 10 minutes.
.spec.timeout is an optional field to specify a timeout duration for any operation like building, applying, health checking, etc. performed during the reconciliation process. Also .spec.retryInterval can be set to retry any failed reconciliation.
.spec.retryInterval is an optional field to specify the interval at which to retry a failed reconciliation. restryInterval: 2m means that Kustomization Controller will retry the reconciliation after 2 min if it detects any failure (failure during the deployment or while performing the health check)
Alternatively, the list of reconciled resources to perform the health check can be limited using spec.healthChecks
.spec.healthChecks is an optional list used to refer to resources for which the controller will perform health checks used to determine the roll-out status of deployed workloads and the Ready status of custom resources.
Note:
If spec.wait is set, spec.healthChecks field is ignored.
A health check entry can reference one of the following types:
- Kubernetes built-in kinds: Deployment, DaemonSet, StatefulSet, PersistentVolumeClaim, Pod, PodDisruptionBudget, Job, CronJob, Service, Secret, ConfigMap, CustomResourceDefinition
- Flux kinds: HelmRelease, HelmRepository, GitRepository, etc.
- Custom resources that are compatible with kstatus
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: cert-manager
spec:
interval: 30m
targetNamespace: cert-manager
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system
path: ./kubernetes/platform/cert-manager/overlays/prod
prune: true
healthChecks:
- apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2
kind: HelmRelease
name: cert-manager
namespace: cert-manager
Kustomization controller will perform health check onlyt for HelmRelease resource named cert-manager in namespace cert-manager.
Health Checks and CRDs
For Custom Resource Definitions that are not compatible with kstatus, Common Expression Language (CEL) expressions can be used to define custom logic for performing health checks.
.spec.healthCheckExprs has to be defined containing a list of resources to be checked and the CEL expressions that need to be used.
The following attributes need to be specified per resource:
apiVersion: The API version of the custom resource. Required.kind: The kind of the custom resource. Required.current: A required CEL expression that returns true if the resource is ready.inProgress: An optional CEL expression that returns true if the resource is still being reconciled.failed: An optional CEL expression that returns true if the resource failed to reconcile. This enable a early failure detection.
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: cert-manager-config
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 30m
targetNamespace: cert-manager
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system
dependsOn:
- name: cert-manager-app
- name: cert-manager-webhook-ionos
- name: external-secrets-config
path: ./kubernetes/platform/cert-manager/config/overlays/prod
prune: true
wait: true
timeout: 15m
healthCheckExprs:
- apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: ClusterIssuer
failed: status.conditions.exists(e, e.type == 'Ready') && status.conditions.filter(e, e.type == 'Ready').all(e, e.status == 'False')
current: status.conditions.exists(e, e.type == 'Ready') && status.conditions.filter(e, e.type == 'Ready').all(e, e.status == 'True')
In this case Cert-manager’s ClusterIssuer custom resource does not follow kstatus and to perform the health check of the resource, we look for specific value in its status conditions.
kubectl get ClusterIssuer ca-issuer -o jsonpath={.status.conditions} | jq .
[
{
"lastTransitionTime": "2025-07-12T11:12:11Z",
"message": "Signing CA verified",
"observedGeneration": 1,
"reason": "KeyPairVerified",
"status": "True",
"type": "Ready"
}
]
Dependencies
.spec.dependsOn is an optional list used to refer to other Kustomization objects that the Kustomization depends on.
The Kustomization is only applied after the referred Kustomizations are ready, i.e. have the Ready condition marked as True. The readiness state of a Kustomization is determined by its last applied status condition.
It can be used jointly with Health checks in the depended objects to control when to start deployment of a specific Kustomization.
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: cert-manager-app
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 30m
targetNamespace: cert-manager
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system
path: ./kubernetes/platform/cert-manager/app/overlays/prod
prune: true
wait: true
timeout: 5m
---
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: cert-manager-webhook-ionos
namespace: flux-system
spec:
interval: 30m
targetNamespace: cert-manager
sourceRef:
kind: GitRepository
name: flux-system
dependsOn:
- name: cert-manager-app
path: ./kubernetes/platform/cert-manager/webhook-ionos/overlays/prod
prune: true
wait: true
timeout: 5m
In the previous example, cert-manager-webhook-ionos application is not deployed till all resources from cert-manager-app are ready.
Note: Dependencies can be defined only across Kustomization resources. It is not possible to establish dependencies on HelmRelease resources. That dependency can be specified using a Health Check on HelmRelease object.
HelmRelease
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: cert-manager
spec:
interval: 30m
chart:
spec:
chart: cert-manager
version: v1.15.1
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: jetstack
namespace: flux-system
releaseName: cert-manager
targetNamespace: cert-manager
install:
remediation:
retries: 3
upgrade:
cleanupOnFail: true
remediation:
strategy: rollback
retries: 3
valuesFrom:
- kind: ConfigMap
name: cert-manager-helm-values
valuesKey: values.yaml
Where:
spec.chart.spec: Define the chart name (spec.chart.spec.chart) and version (spec.chart.spec.version) to install form the corresponding from HelmRepository object (spec.chart.spec.sourceRef)spec.valuesFrom: ConfigMap wherevalues.yamlfile is defined.spec.releaseName: Helm release namespect.targetNamespace: specify the namespace to which the Helm release is deployed. It defaults to the namespace of the HelmRelease.spec.interval:spec.timeout:spec.installandspec.upgrade: define the installation and upgrade policies (retries and rollback strategies)
K3S Cluster Preparation
Disabling K3S Add-Ons
To have the control of any kuberentes configuration deployed in the cluster, K3s add-ons need to be disabled
By default K3s install a HelmChart controller and configure basic Kubernetes networking packages and
- Flannel as Networking plugin, CNI (Container Networking Interface), for enabling pod communications
- CoreDNS providing cluster dns services
- Traefik as ingress controller
- Klipper Load Balancer as embedded Service Load Balancer
K3S master nodes need to be installed with the following additional options:
--flannel-backend=none: to disable Fannel instalation--disable-network-policy: Most CNI plugins come with their own network policy engine, so it is recommended to set –disable-network-policy as well to avoid conflicts.--disable-kube-proxy: to disable kube-proxy installation--disable servicelbto disable default service load balancer installed by K3S (Klipper Load Balancer). Cilium will be used instead.
See complete intallation procedure and other configuration settings in “K3S Installation”
Cluster Bootstrap
Using FluxCD CLI
Flux cli installation
To install flux cli execute the following command:
curl -s https://fluxcd.io/install.sh | sudo bash
Check flux cli installation with
flux -v
Flux version should be printed.
Flux Bootstrap for Github
The flux bootstrap github command deploys the Flux controllers on a Kubernetes cluster and configures the controllers to sync the cluster state from a GitHub repository. Besides installing the controllers, the bootstrap command pushes the Flux manifests to the GitHub repository and configures Flux to update itself from Git.
https://fluxcd.io/flux/installation/bootstrap/github/
flux bootstrap github \
--token-auth \
--owner=ricsanfre \
--repository=fluxcd-test \
--branch=master \
--path=kubernetes/clusters/dev \
--personal
GitHub access requirements
During bootstrapping process, flux bootstrap command need to access the Github repo and perform commits containing flux installation and bootstrapping manifest files.
For accessing the GitHub REST API, the bootstrap command requires a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) with administration permissions.
Note: Bootstrap can be run with a GitHub fine-grained personal access token. The fine-grained PAT must be generated with the following permissions on the cluster repository:
Administration->Access: Read-onlyContents->Access: Read and writeMetadata->Access: Read-only
The GitHub PAT can be exported as an environment variable, before executing flux bootstrap github command:
export GITHUB_TOKEN=<gh-token>
If the GITHUB_TOKEN env var is not set, the bootstrap command will prompt you to type it the token.
You can also supply the token using a pipe e.g. echo "<gh-token>" | flux bootstrap github.
What happens when executing bootstrap command
If the flux bootstrap command executed is:
flux bootstrap github \
--token-auth \
--owner=ricsanfre \
--repository=fluxcd-test \
--branch=master \
--path=kubernetes/clusters/dev \
--personal
the following actions are taken:
-
Flux installation and bootstrap cluster manifest files are committed to Git repo. The following files are created under
kubernetes/cluster/devfolder (pathparameter in bootstrap command)flux-system/gotk-components.yaml: YAML file containing flux instalaltion manifest files-
flux-system/gotk-sync.yaml: Containing GitRepository definition and initial Kustomization application bootstraping--- apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: GitRepository metadata: name: flux-system namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 1m0s ref: branch: master secretRef: name: flux-system url: https://github.com/ricsanfre/fluxcd-test.git --- apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: Kustomization metadata: name: flux-system namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 10m0s path: ./kubernetes/clusters/dev prune: true sourceRef: kind: GitRepository name: flux-system -
flux-system/kustomization.yamlapiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization resources: - gotk-components.yaml - gotk-sync.yaml
The files are written to the Git repo in two different commits
-
Flux controllers are installed into Kubernetes cluster
-
Git PAT is stored in a Kubernetes Secret
GitHub PAT is stored in the cluster as a Kubernetes Secret named
flux-systeminside theflux-systemnamespace. It is not stored in the Git repository.The following secret is automatic created by flux bootstrap command
apiVersion: v1 data: password: <echo $GitHub_PAT | base64> username: <echo "git" | base64 > kind: Secret metadata: name: flux-system namespace: flux-system type: Opaque -
Bootstrap manifest files are applied to the Kubernetes cluster
Manually Bootstrap
To avoid automatic commits to GitHub repo, the following manual installation and bootstrap process can be applied.
-
Create Flux folders structure
mkdir -p clusters/prod/flux-system mkdir -p clusters/prod/config mkdir -p clusters/prod/infra -
Use
flux installto generate flux installation manifest files (gotk-components.yaml) fileflux install \ --export > ./clusters/prod/flux-system/gotk-components.yaml -
Install flux controllers
kubectl apply -f ./clusters/prod/flux-system/gotk-components.yaml -
Create Git secret (This step is only needed in case of private Repos that requires credentials to read the content)
flux create secret git fluxcd \ --url=https://github.com/ricsanfre/fluxcd-test \ --username=username \ --password=password \ --export fluxcd-auth.yamlIt generates a secret file like this:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: fluxcd-test namespace: flux-system stringData: password: password username: usernameApply manifest file generated
kubectl apply -f fluxcd-auth.yaml -
Deploy GitRepository and bootstrap Kustomization application resources
-
Create file
./clusters/prod/config/cluster.yaml--- apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: GitRepository metadata: name: flux-system namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 1m0s ref: branch: master secretRef: name: fluxcd-test url: https://github.com/ricsanfre/fluxcd-test.git --- apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: Kustomization metadata: name: flux-system namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 10m0s path: ./kubernetes/clusters/prod prune: true sourceRef: kind: GitRepository name: flux-system
-
- Apply with
kubectl applycommand
kubectl apply -f ./clusters/prod/config/cluster.yaml
Bootstrap read-only Repo
flux bootstrap command requires Git repository credentials.
Credentials are needed for two purposes:
- To commit flux bootstrap manifest files to the Repo
- If Repo is private, to access the repo. Read-only credentials are needed in this case.
To bootstrap a read-only repo avoiding the need of providing any credential follow the following process:
Bootstrap cluster using manual process instead using flux bootstrap command. Follow the process described before, “Manually Bootstrap”, with this modifications:
- Do not execute step 4
-
In Step 5, configure GitRepository resource without including
secretRefapiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: GitRepository metadata: name: flux-system namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 1m0s ref: branch: master url: https://github.com/ricsanfre/fluxcd-test.git
Important: With Read-only repos some FluxCD functionality won’t work like Automate image updates to Git
FluxCD Operator
The Flux Operator is an open-source project developed by ControlPlane that offers an alternative to the Flux Bootstrap procedure, it removes the operational burden of managing Flux across fleets of clusters by fully automating the installation, configuration, and upgrade of the Flux controllers based on a declarative API.
Flux Operator is a Kubernetes controller for managing the lifecycle of Flux CD. It uses Kubernetes Operator design pattern so, Flux deployment can be configured via customized CRDs.
Install the Flux Operator
Install the Flux Operator in the flux-system namespace, for example using Helm:
helm install flux-operator oci://ghcr.io/controlplaneio-fluxcd/charts/flux-operator \
--namespace flux-system
Install the Flux Controllers
Create a FluxInstance resource named flux in the flux-system namespace to install the latest Flux stable version:
apiVersion: fluxcd.controlplane.io/v1
kind: FluxInstance
metadata:
name: flux
namespace: flux-system
annotations:
fluxcd.controlplane.io/reconcileEvery: "1h"
fluxcd.controlplane.io/reconcileArtifactEvery: "10m"
fluxcd.controlplane.io/reconcileTimeout: "5m"
spec:
distribution:
version: "2.4"
registry: "ghcr.io/fluxcd"
artifact: "oci://ghcr.io/controlplaneio-fluxcd/flux-operator-manifests"
components:
- source-controller
- kustomize-controller
- helm-controller
- notification-controller
cluster:
type: kubernetes
multitenant: false
networkPolicy: true
domain: "cluster.local"
kustomize:
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: "(kustomize-controller|helm-controller)"
patch: |
- op: add
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-
value: --concurrent=10
- op: add
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/args/-
value: --requeue-dependency=5s
Sync from a Git Repository
To sync the cluster state from a Git repository, add the following configuration to the FluxInstance resource:
apiVersion: fluxcd.controlplane.io/v1
kind: FluxInstance
metadata:
name: flux
namespace: flux-system
spec:
sync:
kind: GitRepository
url: "https://github.com/ricsanfre/fluxcd-test.git"
ref: "refs/heads/master"
path: "kubernetes/clusters/prod"
pullSecret: "flux-system" # Not needed if Git repository is public.
# distribution omitted for brevity
If the source repository is private, spec.sync.pullSecret need to be specified and the Kubernetes secret must be created in the flux-system namespace and should contain the credentials to clone the repository:
flux create secret git flux-system \
--url=https://github.com/ricsanfre/fluxcd-test.git \
--username=git \
--password=$GITHUB_TOKEN
Monitor the Flux Installation
To monitor the Flux deployment status, check the FluxReport resource in the flux-system namespace:
kubectl get fluxreport/flux -n flux-system -o yaml
The report is update at regular intervals and contains information about the deployment readiness status, the distribution details, reconcilers statistics, Flux CRDs versions, the cluster sync status and more.
Tip:
flux-instance helm chart can be used as a wrapper for creating FluxInstace custom resource.
Flux CD Git Repo structure
📁 kubernetes
├── 📁 clusters # clusters configuration
│ ├── 📁 bootstrap # Bootstrap configuration files to apply before installed flux
| | ├── helmfile.yaml # Deploy Kuberentes CNI, DNS, etc.
| | ├── 📁 vault # Configure external Vault (external-secrets)
│ ├── 📁 dev # Dev cluster bootstrap files
│ └── 📁 prod # Prod cluster bootstrap files
| ├── 📁 flux-system # Flux controller installation
| ├── 📁 repositories # Flux Source resources
| | ├── kustomization.yaml
| | └── 📁 helm # Flux HelmRepository resources
| | ├── jetstack-helmrepo.yaml
| | └── ...
| ├── 📁 config
| | ├── kustomization.yaml
| | ├── cluster-settings.yaml # Cluster variables (Flux Templates)
| | └── cluster.yaml # Flux GitRepository and Root Kustomization application
| ├── 📁 infra # Flux Kustomization resources for deploying platform services
| | ├── kustomization.yaml
| | ├── cert-manager-app.yaml
| | ├── external-secrets-app.yaml
| | └── ...
| └── 📁 apps # Flux Kustomization resources for deploying apps
├── 📁 platform # platform services
│ ├── 📁 cert-manager # Component for adding opentelemetry config in Helm chart values
│ ├── 📁 external-secrets
│ ├── 📁 longhorn
│ └── 📁 ...
└── 📁 apps # Applications
├── 📁 app1
└── 📁 ...
Following a mono repo approach1, the repo is structured in 3 main directories:
clusters: Flux bootstrap and configuration that is specific to each environment (prod, staging, dev)platform: set of apps and configs installed in all clusters as platform services, and that allow operators to manage the cluster or provide features to the apps. It provides some pre-set variants (components) that clusters can reuse. Configured and installed by infra teams.apps: set of apps that uses services provided byplatform. Installed by tenants (usually developer teams) in a specific cluster.
Applications in platform and apps directory are packaged using Kustomize, providing variants (overlays) for each cluster and reusable-components.
Cluster specific configuration in kubernetes/clusters/<environment>
- Cluster Config (
kubernetes/clusters/<environment>/config)- It contains
cluster.yamlgenerated during manual installation - Cluster settings: ConfigMap containing global variables/secrets
kubernetes/clusters/prod/config/cluster-settings.yaml
--- apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: cluster-settings namespace: flux-system data: CLUSTER_DOMAIN: picluster.ricsanfre.com S3_BACKUP_SERVER: s3.ricsanfre.com - It contains
-
Cluster repositories (helm, OCI, etc.): `kubernetes/clusters/
/repositories HelmRepository resources like (`kubernetes/clusters/
/repositories/helm/jetstack-helmrepo.yaml) --- apiVersion: source.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: HelmRepository metadata: name: jetstack namespace: flux-system spec: url: https://charts.jetstack.io interval: 1h -
Cluster infrastructure applications:
kubernetes/clusters/<environment>/infraIt contains Flux Kustomization resources linked to the Kustomize applications inkubernetes/plaftormKustomization resources like: `kubernetes/clusters/prod/infra/cert-manager-app.yaml--- apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1 kind: Kustomization metadata: name: cert-manager-app namespace: flux-system spec: interval: 30m targetNamespace: cert-manager sourceRef: kind: GitRepository name: flux-system path: ./kubernetes/platform/cert-manager/app/overlays/prod prune: true healthChecks: - apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2 kind: HelmRelease name: cert-manager namespace: cert-managerThis Kustomization resources contain the corresponding dependencies, so Flux now which order to follow when deploying the applications
graph TD; id1>Kustomization: flux-system] -->|Creates| id2>Kustomization: external-secrets-app]; id2>Kustomization: external-secrets-app] -->|Creates| id4[HelmRelease: external-secrets]; id1>Kustomization: flux-system] -->|Creates| id6>Kustomization:csi-external-snapshotter-app]; id1>Kustomization: flux-system] -->|Creates| id7>Kustomization:longhorn-app]; id7>Kustomization:longhorn-app]-->|Creates| id8[HelmRelease: longhorn]; id1>Kustomization: flux-system] -->|Creates| id3>Kustomization: external-secrets-app-config]; id7>Kustomization:longhorn-app] -->|Depends on| id3>Kustomization: external-secrets-app-config]; id7>Kustomization:longhorn-app] -->|Depends on| id6>Kustomization:csi-external-snapshotter-app]; id3>Kustomization: external-secrets-config] -->|Depends on| id2>Kustomization: external-secrets-app]; id3>Kustomization: external-secrets-config] -->|Creates| id5[Cluster Secret Store];
Application Desing Patterns
Kustomize Variants
Use of Kustomize variants (Overlays) to manage with same configuration different environments (dev, staging, production)
Kustomize has two key concepts, Base and Overlays. With Kustomize we can reuse the base files (common manifest YAML files) across all environments (dev, staging, prod, etc.) and overlay (patches) specifications for each of those environments.
Overlaying is the process of creating a customized version of the manifest file (base manifest + overlay manifest = customized manifest file).
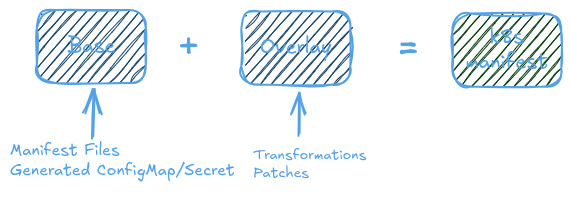
A base is a directory with a kustomization.yaml, which contains a set of resources and associated customization.
base/kustomization.yamlapiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization resources: - manifes1.yaml - manifest2.yaml
An overlay is a directory with a kustomization.yaml that refers to other kustomization directories as its bases
-
overlay/kustomization.yamlapiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization resources: - ../base <transformations>: patches: <patches_section>
Kustomize Components
Use of Kustomize Components to be able to compose Overlays configuration from a set of reusable configurations.
Kustomized Components are reusable kustomizations enabling the composition of Kustomized resources to enabling different application capabilities without the need of define additional overlays. Components can be included from higher-level overlays to create variants of an application, with a subset of its features enabled.
Component has basically the same capabilities as a normal kustomization. The main distinction is that they are evaluated after the resources of the parent kustomization (overlay or component) have been accumulated, and on top of them. This means that:
-
A component with transformers can transform the resources that an overlay has previously specified in the resources field. Components with patches do not have to include the target resource in their resources field.
-
Multiple components can extend and transform the same set of resources sequentially. This is in contrast to overlays, which cannot alter the same base resources, because they clone and extend them in parallel.
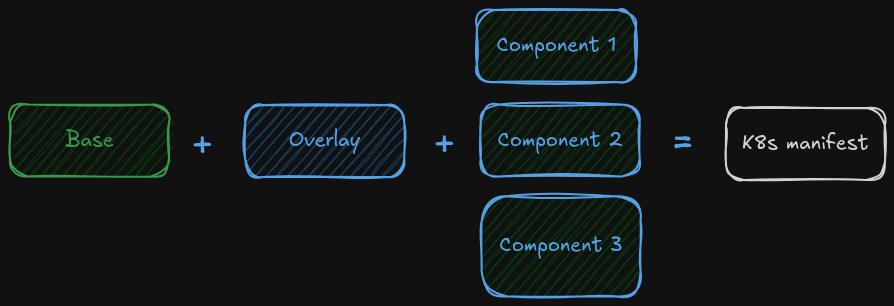
The structure of kustomized application using components can be like this:
📁 app
├── 📁 base # base
│ └── kustomization.yaml
├── 📁 components # components
│ ├── 📁 componentX
│ | └── kustomization.yaml # Additional resources, transformations, patches
│ └── 📁 componentY
│ └── kustomization.yam
└── 📁 overlays
├── 📁 dev # Overlay (dev)
│ └── kustomization.yaml # From base using only componentX
└── 📁 prod # Overay (prod)
└── kustomization.yaml # From base using componentX and componentY
overlays/dev/kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ../../base
components:
- ../../components/componentX
overlays/prod/kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ../../base
components:
- ../../components/componentX
- ../../components/componentY
HelmChart configuration driven by Kustomize Components and Overlays
With Flux, it is possible to use Kustomize ConfigMap generator to trigger a Helm release upgrade every time the encoded values change.
This design pattern means:
HelmReleaseresources getvalues.yamlfile from configMaps- Config Maps containing
values.yamlfiles are automatically generated using Kustomize’s configMap generator. - Config Maps are suffixed with a hash code over its content.
- if configMap content is changed, name is also changed forcing the re-deploy of all resources using that configMap, including the redeploy of HelmRelease
- Stale ConfigMaps, previously generated by Kustomize, will be removed from the cluster by kustomize-controller if pruning is enabled.
See details of this pattern in Flux Helmrealase user guide
Additionally HelmRelease supports to import HelmChart values from more than one yaml source file, merging the content of the files in order (latter files overwriting definition of the previous).
This enables the evolution of the previous design pattern to be able to compose the values.yaml file using Kustomized overlays and components. The following pattern is an evolution of the one described in “Managing Kubernetes the GitOps way by Jeff French”2 to consider also kustomized components
Different configMaps can be generated for base, components and overlays so they are imported in order by HelmRelase, making possible to overwrite base values.yaml with additional configuration provided by Kustomize Components or Kustomized Overlays.
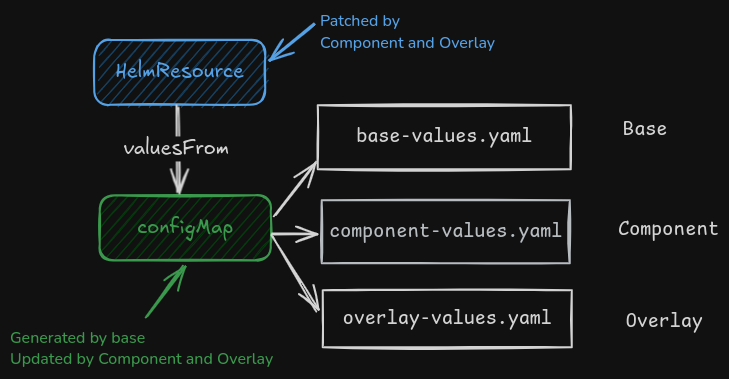
As an example nginx flux application can be defined as follows
📁 nginx
├── 📁 base # base
│ ├── kustomization.yaml # Base Kustomization (ConfigGenerator)
│ ├── helm.yaml # HelmRelease Flux resource
│ ├── kustomizeconfig.yaml # configMap generator config
│ ├── ns.yaml
│ └── values.yaml # Helm chart Base values.yaml
├── 📁 components # components
│ └── 📁 opentelemetry # Component for adding opentelemetry config in Helm chart values
│ ├── helm-patch.yaml # Patch HelmRelase (add new entry in `valuesFrom`)
│ ├── values.yaml # Helm Chart component values.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml # Merge base configMap (new values file entry)
└── 📁 overlays
├── 📁 dev # Overlay (dev)
│ ├── kustomization.yaml # From base not using component (opentelemetry)
| ├── helm-patch.yaml # Patch HelmRelease (adding new entry in `valuesFrom`)
| └── values.yaml # Helm Chart overlay values.yaml
└── 📁 prod # Overay (prod)
├── kustomization.yaml # From base includinc component (opentelemetry)
├── helm-patch.yaml
└── values.yaml
Base configuration
Base defines the namespace manifest file and the HelmRelease resource. Kustomize configMap generator is used to create a configMap containing Helm Chart values.yaml
Where base/helm.yaml contains HelmRelease resource expecting values.yaml in a Config Map
---
apiVersion: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v2
kind: HelmRelease
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx
spec:
interval: 30m
chart:
spec:
chart: ingress-nginx
version: 4.11.2
sourceRef:
kind: HelmRepository
name: ingress-nginx
namespace: flux-system
install:
remediation:
retries: 3
upgrade:
cleanupOnFail: true
remediation:
strategy: rollback
retries: 3
valuesFrom:
- kind: ConfigMap
name: ingress-nginx-helm-values
valuesKey: base-values.yaml
base/kustomization.yaml
Generate automatically a config map ingress-nginx-helm-values with the content of values.yaml file
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ns.yaml
- helm.yaml
configMapGenerator:
- name: ingress-nginx-helm-values
files:
- base-values.yaml=values.yaml
configurations:
- kustomizeconfig.yaml
In the generation it uses a specfic configuration (base/kustomizeconfig.yaml), so fields in the helm chart pointing to the configMap can be updated whenever a new configMap is renamed (new hash is generated)
nameReference:
- kind: ConfigMap
version: v1
fieldSpecs:
- path: spec/valuesFrom/name
kind: HelmRelease
- kind: Secret
version: v1
fieldSpecs:
- path: spec/valuesFrom/name
kind: HelmRelease
Open Telemetry component
This component modify configMap generated in the base configuration, adding a new key otel-values.yaml with the content of components/opentelemetry/values.yaml.
It also patches HelmRelease resource defined in the base adding a new entry into spec.valuesFrom, so new otel-values.yaml can be added
components/opentelemetry/kustomize.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
configMapGenerator:
- name: ingress-nginx-helm-values
behavior: merge
files:
- otel-values.yaml=values.yaml
patches:
- target:
group: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io
kind: HelmRelease
name: ingress-nginx
path: helm-patch.yaml
components/opentelemetry/helm-patch.yaml
- op: add
path: /spec/valuesFrom/-
value:
kind: ConfigMap
name: ingress-nginx-helm-values
valuesKey: otel-values.yaml
components/opentelemetry/values.yaml
controller:
# Enabling Promethues metrics and Service Monitoring
metrics:
enabled: true
serviceMonitor:
enabled: true
# Enabling OTEL traces
opentelemetry:
enabled: true
config:
# Open Telemetry
enable-opentelemetry: "true"
otlp-collector-host: ${otel_collector:=tempo-distributor.tempo.svc.cluster.local}
otlp-service-name: nginx-internal
# Print access log to file instead of stdout
# Separating acces logs from the rest
access-log-path: "/data/access.log"
log-format-escape-json: "true"
log-format-upstream: '{"source": "nginx", "time": $msec, "resp_body_size": $body_bytes_sent, "request_host": "$http_host", "request_address": "$remote_addr", "request_length": $request_length, "request_method": "$request_method", "uri": "$request_uri", "status": $status, "user_agent": "$http_user_agent", "resp_time": $request_time, "upstream_addr": "$upstream_addr", "trace_id": "$opentelemetry_trace_id", "span_id": "$opentelemetry_span_id"}'
# controller extra Volume
extraVolumeMounts:
- name: data
mountPath: /data
extraVolumes:
- name: data
emptyDir: {}
extraContainers:
- name: stream-accesslog
image: busybox
args:
- /bin/sh
- -c
- tail -n+1 -F /data/access.log
imagePullPolicy: Always
resources: {}
terminationMessagePath: /dev/termination-log
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: data
Overlays config
Kustomize overlays uses the base configuration and any additional component. Additionally a new values.yaml file, containing ovelay addtional values, is added to the configMap ingress-nginx-helm-values and the HelmRelease object is patched (as it is in the component part)
overlay/prod/kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
namespace: nginx
resources:
- ../../base
components:
- ../../components/opentelemetry
configMapGenerator:
- name: ingress-nginx-helm-values
behavior: merge
files:
- overlay-values.yaml=values.yaml
patches:
- target:
group: helm.toolkit.fluxcd.io
kind: HelmRelease
name: ingress-nginx
path: helm-patch.yaml
overlays/prod/helm-patch.yaml
- op: add
path: /spec/valuesFrom/-
value:
kind: ConfigMap
name: ingress-nginx-helm-values
valuesKey: overlay-values.yaml
Flux Kustomization Templating
Flux Kustomize provides Post Build Variable Substitution enabling the definition of Flux manifest templates.
In any manifest defined as part of the Kustomization application, a set of variables can be defined. Flux replace these values from static values or from ConfigMaps and Secrets after kustomize build command is executed.
spec.postBuild.substitute or spec.postBuild.subtituteFrom need to be specified in the corresponding Kustomization resource.
Variables have to be specified, as ${var_name:=default_value} in manifest yaml files used by kustomized packaged application.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: apps
labels:
environment: ${cluster_env:=dev}
region: "${cluster_region}"
apiVersion: kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/v1
kind: Kustomization
metadata:
name: apps
spec:
# ...omitted for brevity
postBuild:
substitute:
cluster_env: "prod"
cluster_region: "eu-central-1"
substituteFrom:
- kind: ConfigMap
name: cluster-vars
# Use this ConfigMap if it exists, but proceed if it doesn't.
optional: true
- kind: Secret
name: cluster-secret-vars
# Fail if this Secret does not exist.
Important:
Fux executes substitution logic after the execution of kustomize build command.
If a variable is included in the content of a ConfigMap that is auto-generated by Kustomize, as it might happens when using design pattern to generate helm values.yaml file, the content of the variable will not be used to generate the hash suffix for the configMap. So, if variable content is changed, no new configMap, with new name, will be generated since the hash won’t be different.
See further details in this flux discussion
Testing variable substitution
Output generated by flux can be tested using flux envsubst command.
$ export cluster_region=eu-central-1
$ kustomize build . | flux envsubst --strict
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: apps
labels:
environment: dev
region: eu-central-1
Skip var substitution for certain resources
Environment variables can be defined in different manifest fields (i.e container commands or environment variables whose values are obtained from ConfigMaps). If those environement variable s are defined using ${var} notation, Flux will try to substitute the variable and it will replace by empty string if no definition is found.
If you want to avoid var substitutions in scripts embedded in ConfigMaps or container commands, $var notation must be used instead of ${var}. If you want to keep the curly braces you can use $${var} which will print out ${var}.
All the undefined variables in the format ${var} will be substituted with an empty string unless a default value is provided e.g. ${var:=default}.
Variable substitution can be disabled for certain resources by either labelling or annotating them with:
kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/substitute: disabled
Flux and Kubernetes Jobs
Additional considerations have to be made when managing Kubernetes Jobs with Flux.
By default, if you were to have Flux reconcile a Job resource, it would apply it once to the cluster, the Job would create a Pod that can either error or run to completion. Attempting to update the Job manifest after it has been applied to the cluster will not be allowed, as changes to the Job spec.Completions, spec.Selector and spec.Template are not permitted by the Kubernetes API. To be able to update a Kubernetes Job, the Job has to be recreated by first being removed and then reapplied to the cluster.3
Job resources annotated with kustomize.toolkit.fluxcd.io/force: enabled will be automatically recreated by FluxCD whenever there are changes to be applied.
Observability
Metrics
Flux has native support for Prometheus metrics to provide insights into the state of the Flux components. These can be used to set up monitoring for the Flux controllers. In addition, Flux Custom Resource metrics can also be collected leveraging tools like kube-state-metrics.4
Prometheus Integration
Flux Controllers Monitoring
Flux Controllers expose Prometheus metrics at port 8080 in the standard /metrics path.
When using Kube-Prometheus-Stack, Prometheus Operator’s PodMonitor resource can be created to start scraping metrics from Flux Controllers components
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: PodMonitor
metadata:
name: flux-system
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/part-of: flux
app.kubernetes.io/component: monitoring
spec:
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- flux-system
selector:
matchExpressions:
- key: app
operator: In
values:
- helm-controller
- source-controller
- kustomize-controller
- notification-controller
- image-automation-controller
- image-reflector-controller
podMetricsEndpoints:
- port: http-prom
Flux Custom Resources Monitoring
Flux Custom Resources metrics can be monitored using kube-state-metrics, which it is installed as part of Kube-Prometheus-Stack.
When using Kube-Prometheus-Stack, add values to helm chart configuration defined in Flux monitoring example: kube-state-metrics-config.yaml
Grafana Dashboards
Flux provides 2 Grafana Dashboards to display metrics collected by Prometheus available at Flux monitoring example Github repo
- Control plane dashboard: control-plane.json
- Cluster reconciliation dashboard: cluster.json
The following configuration can be added to Grafana’s Helm Chart so a FluxCD’s dashboard provider can be created and dashboards can be automatically downloaded from GitHub repository
dashboardProviders:
dashboardproviders.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
providers:
- name: flux
orgId: 1
folder: Flux
type: file
disableDeletion: false
editable: true
options:
path: /var/lib/grafana/dashboards/flux-folder
# Dashboards
dashboards:
flux:
flux-cluster:
url: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fluxcd/flux2-monitoring-example/main/monitoring/configs/dashboards/cluster.json
datasource: Prometheus
flux-control-plane:
url: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fluxcd/flux2-monitoring-example/main/monitoring/configs/dashboards/control-plane.json
datasource: Prometheus
-
All your Kubernetes manifests in a single Git repository. The various environments specific configs are all stored in the same branch Flux documentation: Ways of structuring your repositories ↩
-
This design pattern explained in the following webinar.