Log Analytics (Elasticsearch and Kibana)
Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes (ECK) Operator is an implementation of Kubernetes Operator design pattern for deploying Elastic stack applications: ElasticSearch, Kibana, Logstash and other applications from Elastic ecosystem.
ECK Operator will be used to deploy Elasticsearh and Kibana.
ECK Operator installation
- Step 1: Add the Elastic repository:
helm repo add elastic https://helm.elastic.co - Step2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update - Step 3: Create namespace
kubectl create namespace elastic - Step 3: Install ECK operator in the
elasticnamespacehelm install elastic-operator elastic/eck-operator --namespace elastic - Step 4: Monitor operator logs:
kubectl -n elastic logs -f statefulset.apps/elastic-operator
Elasticsearch installation
Basic instructions can be found in ECK Documentation: “Deploy and elasticsearch cluster”
-
Step 1: Create a manifest file containing basic configuration: one node elasticsearch using Longhorn as storageClass and 5GB of storage in the volume claims.
apiVersion: elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/v1 kind: Elasticsearch metadata: name: efk namespace: elastic spec: version: 8.15.0 nodeSets: - name: default count: 1 # One node elastic search cluster config: node.store.allow_mmap: false # Disable memory mapping volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: elasticsearch-data spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 5Gi storageClassName: ${STORAGE_CLASS} http: tls: # Disabling TLS automatic configuration. selfSignedCertificate: disabled: trueNote:
Substitute variables (
${var}) in the above yaml file before deploying mangifest file.- Replace
${STORAGE_CLASS}by storage class name used (i.e.longhorn,local-path, etc.)
-
About Virtual Memory configuration (mmap)
By default, Elasticsearch uses memory mapping (
mmap) to efficiently access indices. To disable this default mechanism add the following configuration option:node.store.allow_nmap: falseUsually, default values for virtual address space on Linux distributions are too low for Elasticsearch to work properly, which may result in out-of-memory exceptions. This is why
mmapis disable.For production workloads, it is strongly recommended to increase the kernel setting
vm.max_map_countto 262144 and leavenode.store.allow_mmapunset.See further details in ECK Documentation: “Elastisearch Virtual Memory”
-
About Persistent Storage configuration
Longhorn is configured for Elastisearch POD’s persistent volumes
volumeClaimTemplates: - metadata: name: elasticsearch-data spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteOnce resources: requests: storage: 5Gi storageClassName: ${STORAGE_CLASS}See how to configure PersistenVolumeTemplates for Elasticsearh using this operator in ECK Documentation: “Volume claim templates”
-
Disable TLS configuration
http: tls: selfSignedCertificate: disabled: trueBy default ECK configures secured communications with auto-signed SSL certificates. Access to its service endpoint on port 9200 is only available through https.
Disabling TLS automatic configuration in Elasticsearch HTTP server enables Cluster Service Mesh to gather more statistics about connections. Service Mesh is parsing plain text traffic (HTTP) instead of encrypted (HTTPS).
Cluster service mesh will enforce secure communications using TLS between all PODs.
-
About limiting resources assigned to ES
In Kubernetes, limits in the consumption of resources (CPU and memory) can be assigned to PODs. See “Kubernetes Doc - Resource Management for Pods and Containers”.
resource requestsdefines the minimum amount of resources that must be available for a Pod to be scheduled;resource limitsdefines the maximum amount of resources that a Pod is allowed to consume.When you specify the
resource requestfor containers in a Pod, the kube-scheduler uses this information to decide which node to place the Pod on. When you specify aresource limitfor a container, the kubelet enforces those limits so that the running container is not allowed to use more of that resource than the limit you set. The kubelet also reserves at least the request amount of that system resource specifically for that container to use.In case of using ECK Operator is it recommended to specify those resource limits and resource request to each of the Objects created by the Operator. See details on how to setup those limits in ECK Documentation - Manage compute resources.
For example memory heap assigned to JVM is calculated based on that resource limits, “The heap size of the JVM is automatically calculated based on the node roles and the available memory. The available memory is defined by the value of
resources.limits.memoryset on the elasticsearch container in the Pod template, or the available memory on the Kubernetes node is no limit is set”.By default, ECK does not specify any limit to CPU resource and it defines
resources.limits.memoryfor ElasticSearch POD set to 2GB.In production environment this default limit should be increased. In lab environments where memory resources are limited it can be decreased to reduce ES memory footprint.
In both scenarios, the limit can be changed in in
Elasticsearchobject (podTemplatesection).podTemplate: # Limiting Resources consumption spec: containers: - name: elasticsearch resources: requests: memory: 1Gi limits: memory: 1Gi
- Replace
-
Step 2: Apply manifest
kubectl apply -f manifest.yml -
Step 3: Check Elasticsearch status
kubectl get elasticsearch -n elastic NAME HEALTH NODES VERSION PHASE AGE efk green 1 8.15.0 Ready 139mNote:
Elasticsearch status
HEALTH=greenindicates that Elasticsearch is running and healthy,PHASE=Readyindicates that the server is up and running
Elasticsearch authentication
By default ECK configures user authentication to access elasticsearch service. ECK defines a default admin esaticsearch user (elastic) and with a password which is stored within a kubernetes Secret.
Both to access elasticsearch from Kibana GUI or to configure Fluentd collector to insert data, elastic user/password need to be provided.
Password is stored in a kubernetes secret (<efk_cluster_name>-es-elastic-user). Execute this command for getting the password
kubectl get secret -n elastic efk-es-elastic-user -o=jsonpath='{.data.elastic}' | base64 --decode; echo
File-based Authentication
ECK has the capability to define additional custom users and roles. Custom users are added using ES File-based Authentication. Custom roles can also be added using ES file-based roles
Important:
Users/roles including in file realm cannot be managed using the user APIs, or using the Kibana Management > Security > Users/Roles pages. File based used/roles are defined at ES node level. All nodes of a cluster should have same users/roles configured. ECK operator guarantees that all nodes of the cluster have the same file-based users/roles.
See Users and roles from elastic cloud-on-k8s documentation.
To allow fluentd and prometheus exporter to access our elasticsearch cluster, we can define two role that grants the necessary permission for the two users we will be creating (fluentd, prometheus).
-
Step 1: Create Secrets containing roles definitions
Fluentd user role:
kind: Secret apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: es-fluentd-roles-secret namespace: elastic stringData: roles.yml: |- fluentd_role: cluster: ['manage_index_templates', 'monitor', 'manage_ilm'] indices: - names: [ '*' ] privileges: [ 'indices:admin/create', 'write', 'create', 'delete', 'create_index', 'manage', 'manage_ilm' ]Prometheus Exporter user role:
kind: Secret apiVersion: v1 metadata: name: es-prometheus-roles-secret namespace: elastic stringData: roles.yml: |- prometheus_role: cluster: [ 'monitor', 'monitor_snapshot' ] indices: - names: [ '*' ] privileges: [ 'monitor', 'view_index_metadata' ] -
Step 2. Create the Secrets containing user name, password and mapped role
Fluentd user:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: es-fluentd-user-file-realm namespace: elastic type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth data: username: <`echo -n 'fluentd' | base64`> password: <`echo -n 'supersecret' | base64`> roles: <`echo -n 'fluentd_role' | base64`>Prometheus exporter user:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: es-prometheus-user-file-realm namespace: elastic type: kubernetes.io/basic-auth data: username: <`echo -n 'prometheus' | base64`> password: <`echo -n 'supersecret' | base64`> roles: <`echo -n 'prometheus_role' | base64`> -
Step 3: Modify Elasticsearch yaml file created in step 1 of ES installation.
Add the following lines to ElasticSearch manifest file:
apiVersion: elasticsearch.k8s.elastic.co/v1 kind: Elasticsearch metadata: name: efk namespace: elastic spec: auth: roles: - secretName: es-fluentd-roles-secret - secretName: es-prometheus-roles-secret fileRealm: - secretName: es-fluentd-user-file-realm - secretName: es-prometheus-user-file-realm ...
In addition to the elastic user we can also create an super user account for us to login, we can create the account just like how we created the fluentd or prometheus user, but instead with the role set to superuser.
Accesing Elasticsearch from outside the cluster
By default Elasticsearh HTTP service is accesible through Kubernetes ClusterIP service types (only available within the cluster). To make it available outside the cluster Ingress NGINX can be configured to enable external communication with Elasicsearh server.
This exposure will be useful for doing remote configurations on Elasticsearch through its API from pimaster node. For example: to configure backup snapshots.
-
Step 1. Create the ingress rule manifest
--- # HTTPS Ingress apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: elasticsearch-ingress namespace: elastic annotations: # Enable cert-manager to create automatically the SSL certificate and store in Secret cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: ca-issuer cert-manager.io/common-name: elasticsearch.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} spec: ingressClassName: nginx tls: - hosts: - elasticsearch.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} secretName: elasticsearch-tls rules: - host: elasticsearch.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: efk-es-http port: number: 9200Note:
Substitute variables (
${var}) in the above yaml file before deploying manifest.- Replace
${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}by the domain name used in the cluster. For example:homelab.ricsanfre.com.
Ingress Controller NGINX exposes elasticsearch server as
elasticsearch.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}virtual host, routing rules are configured for redirecting all incoming HTTP traffic to HTTPS and TLS is enabled using a certificate generated by Cert-manager.See “Ingress NGINX Controller - Ingress Resources Configuration” for furher details.
ExternalDNS will automatically create a DNS entry mapped to Load Balancer IP assigned to Ingress Controller, making ElasticSearch service available at `elasticsearch.{$CLUSTER_DOMAIN}. Further details in “External DNS - Use External DNS”
- Replace
-
Step 2: Apply manifest
kubectl apply -f manifest.yml -
Step 3. Access to Elastic HTTP service
UI can be access through http://elasticsearch.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} using loging
elasticand the password stored in<efk_cluster_name>-es-elastic-user.It should shows the following output (json message)
{ "name" : "efk-es-default-0", "cluster_name" : "efk", "cluster_uuid" : "WTb_fupJRl27biWOnJY5tQ", "version" : { "number" : "8.15.0", "build_flavor" : "default", "build_type" : "docker", "build_hash" : "1a77947f34deddb41af25e6f0ddb8e830159c179", "build_date" : "2024-08-05T10:05:34.233336849Z", "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "9.11.1", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "7.17.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "7.0.0" }, "tagline" : "You Know, for Search" }
Kibana installation
-
Step 1. Create a manifest file
apiVersion: kibana.k8s.elastic.co/v1 kind: Kibana metadata: name: kibana namespace: elastic spec: version: 8.15.0 count: 1 elasticsearchRef: name: "efk" http: # NOTE disabling kibana automatic TLS configuration tls: selfSignedCertificate: disabled: true - Step 2: Apply manifest
kubectl apply -f manifest.yml - Step 3: Check kibana status
kubectl get kibana -n elastic NAME HEALTH NODES VERSION AGE efk green 1 8.15.0 171mNote:
Kibana status
HEALTH=greenindicates that Kibana is up and running.
Ingress rule for Kibana
Make accesible Kibana UI from outside the cluster through Ingress Controller
-
Step 1. Create the ingress rule manifest
--- # HTTPS Ingress apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: name: kibana-ingress namespace: elastic annotations: # Enable cert-manager to create automatically the SSL certificate and store in Secret cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: ca-issuer cert-manager.io/common-name: kibana.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} spec: ingressClassName: nginx tls: - hosts: - kibana.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} secretName: kibana-tls rules: - host: kibana.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN} http: paths: - path: / pathType: Prefix backend: service: name: efk-kb-http port: number: 5601Note:
Substitute variables (
${var}) in the above yaml file before deploying manifest.- Replace
${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}by the domain name used in the cluster. For example:homelab.ricsanfre.com.
Ingress Controller NGINX exposes Kibana server as
kibana.${CLUSTER_DOMAIN}virtual host, routing rules are configured for redirecting all incoming HTTP traffic to HTTPS and TLS is enabled using a certificate generated by Cert-manager.See “Ingress NGINX Controller - Ingress Resources Configuration” for furher details.
ExternalDNS will automatically create a DNS entry mapped to Load Balancer IP assigned to Ingress Controller, making Kibana service available at `kibana.{$CLUSTER_DOMAIN}. Further details in “External DNS - Use External DNS”
- Replace
- Step 2: Apply manifest
kubectl apply -f manifest.yml -
Step 3. Access to Kibana UI
UI can be access through http://kibana.picluster.ricsanfre.com using loging
elasticand the password stored in<efk_cluster_name>-es-elastic-user.Execute the following command to get
elasticuser passwordkubectl get secret efk-es-elastic-user -o jsonpath='{.data.elastic}' -n elastic | base64 -d;echo
Initial Kibana Setup (DataView configuration)
Kibana’s DataView must be configured in order to access Elasticsearch data.
Note:
This configuration must be done once data from fluentd has been inserted in ES: A index (fluentd-*) containing data has been created.
-
Step 1: Open Kibana UI
Open a browser and go to Kibana’s URL (kibana.picluster.ricsanfre.com)
-
Step 2: Open “Management Menu”
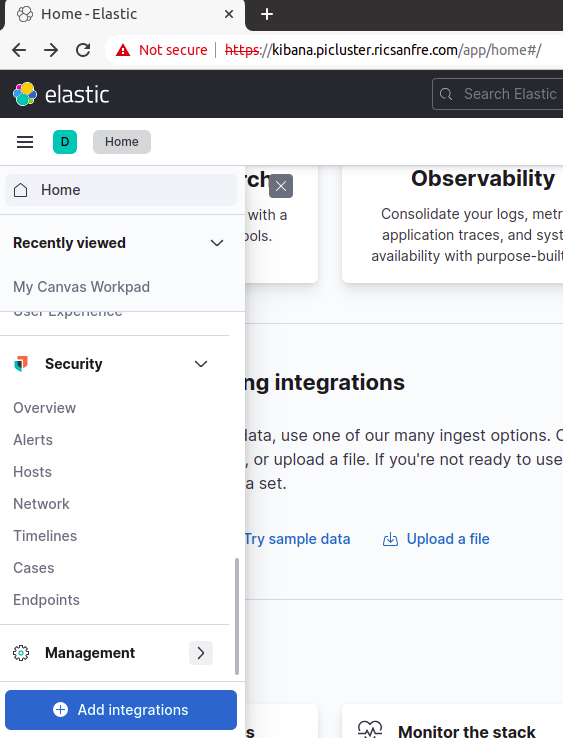
-
Step 3: Select “Kibana - Data View” menu option and click on “Create data view”
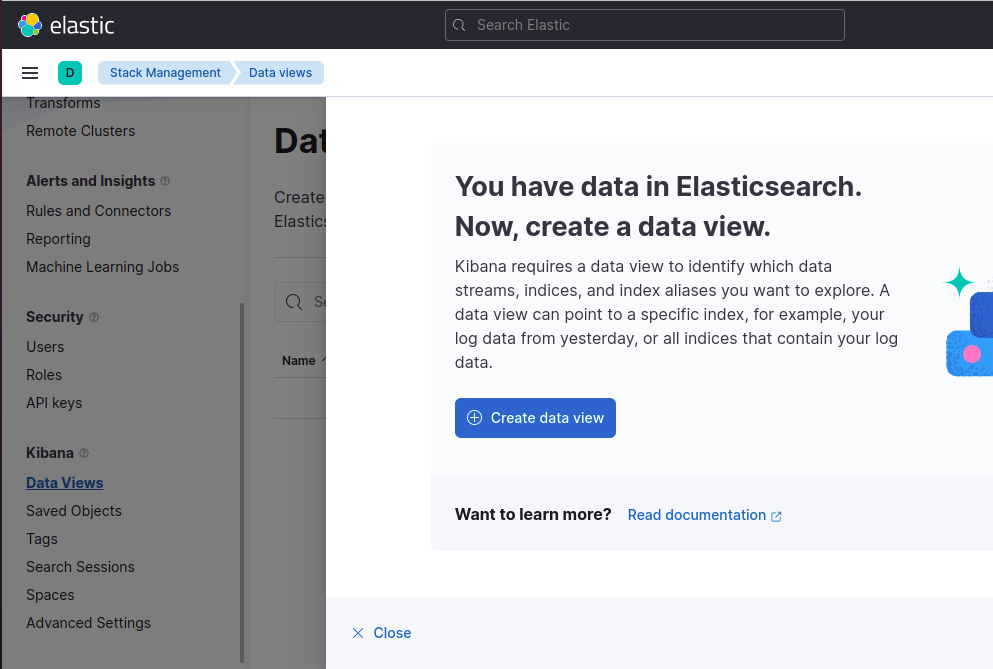
-
Step 4: Set index pattern to fluentd-* and timestamp field to @timestamp and click on “Create Index”
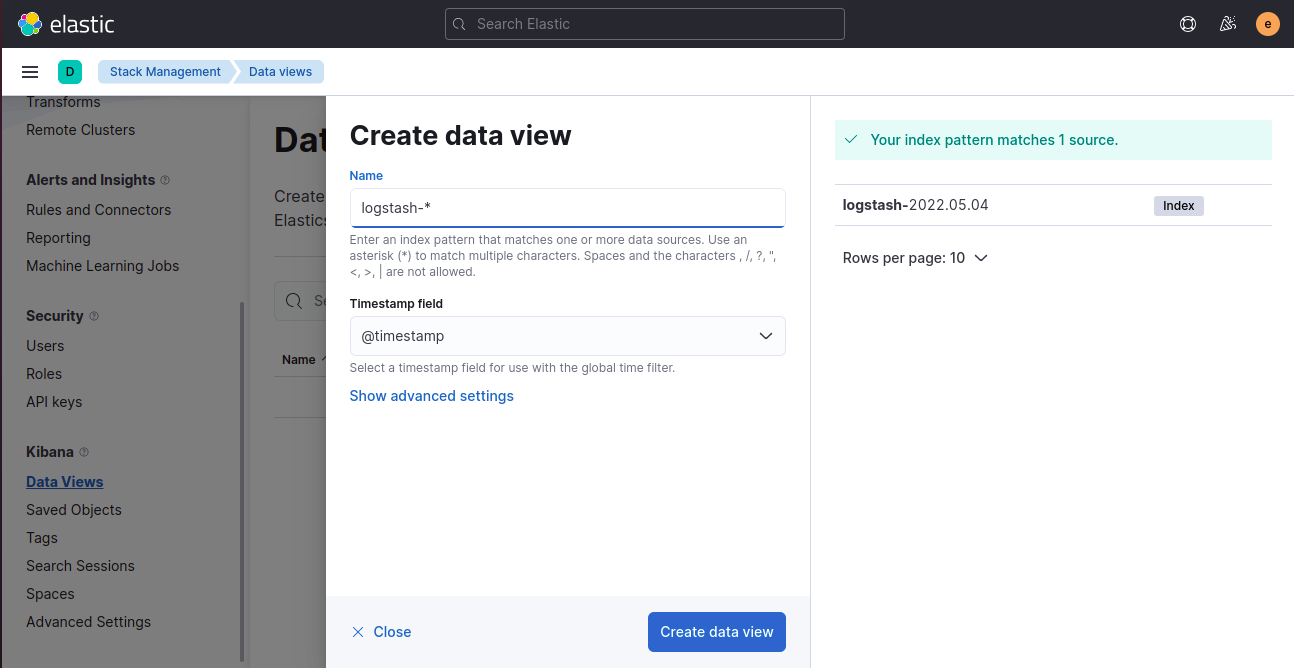
Automation using API
Kibana’s dataview can be automatically creatred using Kibana’s API DataView endpoint.
A Kubernetes Job can be created to automatically invoke API to create the required API.
The following configMap contains two scripts to be executed by the Job:
wait-for-kibana.sh: it test the connection to Kibana, and wait till Kibana is availablecreate-data-view.sh: Create a Dataview using Kibana API.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: kibana-config-data
data:
wait-for-kibana.sh: |
#!/bin/sh
# Wait for Kibana to be available & healthy
echo "Testing connection to Kibana"
until $(curl -k -X GET http://$KIBANA_URL:$KIBANA_PORT/_cluster/health); do sleep 5; done
until [ "$(curl -k -X GET http://$KIBANA_URL:$KIBANA_PORT/_cluster/health | wc -l)" == "0" ]
do sleep 5
done
create-data-view.sh: |
#!/bin/sh
#Import data view
echo "Importing data_view..."
curl -u elastic:$ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD \
-X POST http://$KIBANA_URL:$KIBANA_PORT/api/data_views/data_view \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json; Elastic-Api-Version=2023-10-31' \
-H 'kbn-xsrf: string' \
-d '
{
"data_view": {
"name": "fluentd",
"title": "fluentd-*",
"timeFieldName": "@timestamp"
}
}
'
The Job is the following:
apiVersion: batch/v1
kind: Job
metadata:
name: kibana-config-job
spec:
parallelism: 1
completions: 1
template:
spec:
restartPolicy: Never
initContainers:
- name: wait-for-kibana
image: alpine/curl:latest
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
env:
- name: KIBANA_URL
value: efk-kb-http
- name: KIBANA_PORT
value: "5601"
command: ["/bin/sh","/kibana/wait-for-kibana.sh"]
volumeMounts:
- name: kibana-config-data
mountPath: /kibana/
containers:
- name: kibana-config-job
image: alpine/curl:latest
env:
- name: ELASTICSEARCH_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: efk-es-elastic-user
key: elastic
- name: KIBANA_URL
value: efk-kb-http
- name: KIBANA_PORT
value: "5601"
command: ["/bin/sh","/kibana/create-data-view.sh"]
volumeMounts:
- name: kibana-config-data
mountPath: /kibana/
volumes:
- name: kibana-config-data
configMap:
name: kibana-config-data
defaultMode: 0777
Observability
Metrics
Prometheus Integration via Elasticsearh exporter
In order to monitor elasticsearch with prometheus, prometheus-elasticsearch-exporter need to be installed.
For doing the installation prometheus-elasticsearch-exporter official helm will be used.
-
Step 1: Add the prometheus community repository
helm repo add prometheus-community https://prometheus-community.github.io/helm-charts -
Step 2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository
helm repo update -
Step 3: Create values.yml for configuring the helm chart
--- # Elastic search password from secret extraEnvSecrets: ES_USERNAME: secret: es-prometheus-user-file-realm key: username ES_PASSWORD: secret: es-prometheus-user-file-realm key: password # Elastic search URI es: uri: http://efk-es-http:9200 # Enable Service Monitor serviceMonitor: ## If true, a ServiceMonitor CRD is created for a prometheus operator ## https://github.com/coreos/prometheus-operator ## enabled: true
This config passes ElasticSearch API endpoint (uri) and the needed credentials through environement variables(ES_USERNAME and ES_PASSWORD). The es-prometheus-user-file-realm secret was created in section Elasticsearch authentication.
-
Step 3: Install prometheus-elasticsearh-exporter in the
elasticnamespace with the overriden valueshelm install -f values.yml prometheus-elasticsearch-exporter prometheus-community/prometheus-elasticsearch-exporter --namespace elastic
When deployed, the exporter generates a Kubernetes Service exposing prometheus-elasticsearch-exporter metrics endpoint (/metrics on port 9108)
It can be tested with the following command:
curl prometheus-elasticsearch-exporter.logging.svc.cluster.local:9108/metrics
# HELP elasticsearch_breakers_estimated_size_bytes Estimated size in bytes of breaker
# TYPE elasticsearch_breakers_estimated_size_bytes gauge
elasticsearch_breakers_estimated_size_bytes{breaker="eql_sequence",cluster="efk",es_client_node="true",es_data_node="true",es_ingest_node="true",es_master_node="true",host="10.42.2.20",name="efk-es-default-0"} 0
elasticsearch_breakers_estimated_size_bytes{breaker="fielddata",cluster="efk",es_client_node="true",es_data_node="true",es_ingest_node="true",es_master_node="true",host="10.42.2.20",name="efk-es-default-0"} 0
elasticsearch_breakers_estimated_size_bytes{breaker="inflight_requests",cluster="efk",es_client_node="true",es_data_node="true",es_ingest_node="true",es_master_node="true",host="10.42.2.20",name="efk-es-default-0"} 0
elasticsearch_breakers_estimated_size_bytes{breaker="model_inference",cluster="efk",es_client_node="true",es_data_node="true",es_ingest_node="true",es_master_node="true",host="10.42.2.20",name="efk-es-default-0"} 0
...
Integration with Kube-prom-stack
Providing serviceMonitor.enabled: true to the helm chart values.yaml file, corresponding Prometheus Operator’s resource, ServiceMonitor, so Kube-Prometheus-Stack can automatically start scraping metrics form this endpoint
Grafana Dashboards
Elasticsearh exporter dashboard sample can be donwloaded from prometheus-elasticsearh-exporter repo.
Dashboard can be automatically added using Grafana’s dashboard providers configuration. See further details in “PiCluster - Observability Visualization (Grafana): Automating installation of community dasbhoards
Add following configuration to Grafana’s helm chart values file:
# Configure default Dashboard Provider
# https://grafana.com/docs/grafana/latest/administration/provisioning/#dashboards
dashboardProviders:
dashboardproviders.yaml:
apiVersion: 1
providers:
- name: infrastructure
orgId: 1
folder: "Infrastructure"
type: file
disableDeletion: false
editable: true
options:
path: /var/lib/grafana/dashboards/infrastructure-folder
# Add dashboard
# Dashboards
dashboards:
infrastructure:
elasticsearch:
url: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/prometheus-community/elasticsearch_exporter/master/examples/grafana/dashboard.json
datasource: Prometheus