Kubernetes development environment
The development setup is the following:
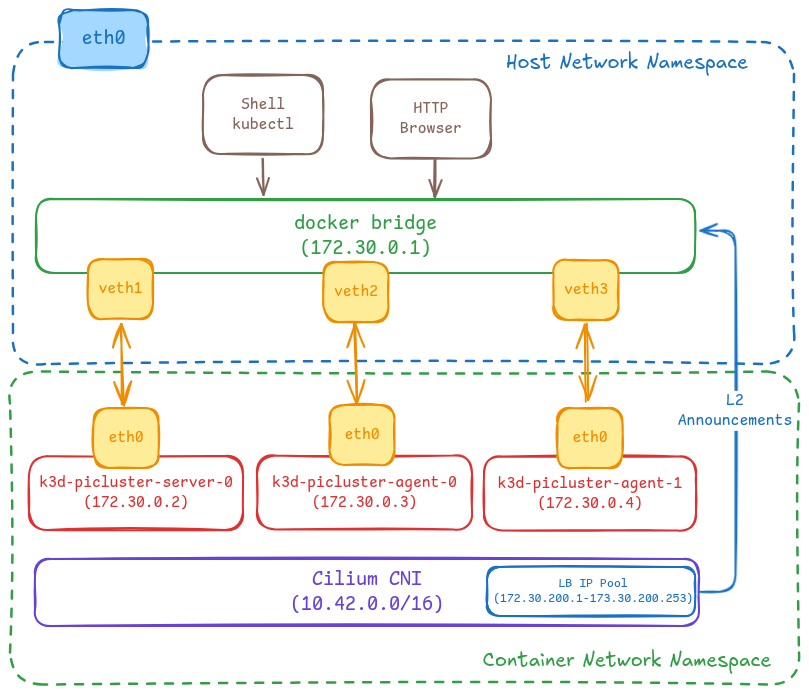
- A dedicated docker network is configured for the cluster
- k3d cluster installed disabling flannel CNI, kube-proxy and load balancer.
- Cilium is installed as CNI which also takes care of the routing which was handled by kube-proxy.
- Cilium L2-LB awareness is enabled, and a set of IP’s are configured for Loadbalancers services and advertised via L2 announcements.
- Docker cluster nodes and Load balancer Kubernetes services are reachable from local host through docker network
Preparing the development environment
The following need to be installed in your local development environment
- Docker
- K3D
- kubectl
- helm
Docker
Follow official installation guide.
-
Step 1. Uninstall old versions of docker
for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done -
Step 2. Install packages to allow apt to use a repository over HTTPS
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install \ apt-transport-https \ ca-certificates \ curl \ gnupg \ lsb-release -
Step 3. Add Docker’s official GPG key
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc -
Step 4: Add x86_64 repository
echo \ "deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \ $(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null -
Step 5: Install Docker Engine
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -
Step 6: Enable Docker management with a non-privileged user
-
Create docker group
sudo groupadd docker -
Add user to docker group
sudo usermod -aG docker $USER
-
-
Step 7: Configure Docker to start on boot
sudo systemctl enable docker.service sudo systemctl enable containerd.service -
Step 8: Configure docker daemon.
-
Edit file
/etc/docker/daemon.jsonSet storage driver to overlay2 and to use systemd for the management of the container’s cgroups. Optionally default directory for storing images/containers can be changed to a different disk partition (example /data). Documentation about the possible options can be found here
{ "exec-opts": ["native.cgroupdriver=systemd"], "log-driver": "json-file", "log-opts": { "max-size": "100m" }, "storage-driver": "overlay2", "data-root": "/data/docker" } -
Restart docker
sudo systemctl restart docker
-
K3D
Follow official K3D installation guide.
-
Step 1. Uninstall old versions of docker
wget -q -O - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/k3d-io/k3d/main/install.sh | bash -
Step 3. Check k3d version installed
$ k3d version k3d version v5.7.5 k3s version v1.30.6-k3s1 (default)
Kubectl
Follow official kubectl installation guide
-
Step 1: Download latest stable version
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" -
Step 2: Install kubectl in /usr/local/bin
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl -
Step 3: Check version installed
$ kubectl version --client --output=yaml clientVersion: buildDate: "2024-06-11T20:29:44Z" compiler: gc gitCommit: 39683505b630ff2121012f3c5b16215a1449d5ed gitTreeState: clean gitVersion: v1.30.2 goVersion: go1.22.4 major: "1" minor: "30" platform: linux/amd64 kustomizeVersion: v5.0.4-0.20230601165947-6ce0bf390ce3
Helm
-
Step 1: Download helm install script
curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 $ chmod 700 get_helm.sh $ ./get_helm.sh -
Step 2: Give it executable permissions
chmod 700 get_helm.sh -
Step 3: Install helm
./get_helm.sh -
Step 4: Check version
$ helm version version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.15.3", GitCommit:"3bb50bbbdd9c946ba9989fbe4fb4104766302a64", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.22.5"}
Creating dockerized k3s cluster
k3s cluster can be created using K3D. The cluster will be configured with same options as production environment:
- CNI cillium is used, instead of default Flannel
- All K3s add-ons are not installed (traefik, helmcontroller, localpath, coredns, etc.)
- kube-proxy is disabled (Cilium Kube-proxy replacement feature will be used)
- Cilium L2 LB announcement will be used
Prerequisites
Enable kernel modules
Since cilium uses IPtables to write routes to kernel, we need to enable additional kernel modules
sudo modprobe -v iptable_filter
sudo modprobe -v ip_tables
sudo modprobe -v iptable_mangle
sudo modprobe -v iptable_raw
sudo modprobe -v iptable_nat
sudo modprobe -v xt_socket
Add this configuration in kernel modules configuration file to persist the modules after restart
echo "iptable_filter
ip_tables
iptable_mangle
iptable_raw
iptable_nat
xt_socket" | sudo tee /etc/modules-load.d/modules.conf
Ensure sysctl parameters are enabled
echo "net.core.devconf_inherit_init_net=1
net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max=196608
net.ipv4.conf.all.forwarding = 1 | sudo tee /etc/sysctl.d/01-sysctl.conf > /dev/null
sudo sysctl -p
Creating docker network
A specific docker network, 172.30.0.0/16, will be created for the k3d dev environment
docker network create \
--driver bridge \
--subnet "172.30.0.0/16" \
--gateway "172.30.0.1" \
--ip-range "172.30.0.0/16" \
"picluster"
Creating K3D cluster
-
Step 1. Create k3d-config.yaml file
apiVersion: k3d.io/v1alpha5 kind: Simple metadata: name: picluster servers: 1 agents: 2 kubeAPI: # same as `--api-port myhost.my.domain:6445` (where the name would resolve to 127.0.0.1) hostIP: 127.172.30.1 # where the Kubernetes API will be listening on hostPort: "6443" # Setting version of k3s image: rancher/k3s:v1.30.6-k3s1 # Setting docker network to be used network: picluster options: # Disable Load balancer k3d: disableLoadbalancer: true # Extra arguments for k3s k3s: extraArgs: - arg: --tls-san=127.0.0.1 nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable helmcontroller - arg: --disable-helm-controller nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable coreDNS - arg: --disable=coredns nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable traefik - arg: --disable=traefik nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable servicelb - arg: --disable=servicelb nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable local storage - arg: --disable=local-storage nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable metric server - arg: --disable=metrics-server nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable network-policy - arg: --disable-network-policy nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable kube-proxy - arg: --disable-kube-proxy nodeFilters: - server:* # Disable flannel-backend - arg: --flannel-backend=none nodeFilters: - server:* # Adding cluster PODs and Services CIDRs - arg: --cluster-cidr=10.42.0.0/16 nodeFilters: - server:* - arg: --service-cidr=10.43.0.0/16 nodeFilters: - server:* # Exposing metrics - arg: --kube-controller-manager-arg=bind-address=0.0.0.0 nodeFilters: - server:* - arg: --kube-scheduler-arg=bind-address=0.0.0.0 nodeFilters: - server:* kubeconfig: updateDefaultKubeconfig: true switchCurrentContext: true-
This config 3 nodes cluster is created (1 control plane node and 2 workers) connected to docker network created before (
picluster)- k3d-picluster-server-0, with IP 172.30.0.2
- k3d-picluster-agent-0, with IP 172.30.0.3
- k3d-picluster-agent-1, with IP 172.30.0.4
-
k3s version is defined through the corresponding docker image label (
image: rancher/k3s:v1.30.6-k3s1) -
Following k3s services are disabled:
kube-proxy,traefik,servicelb,flannelandnetwork-policy -
k3d default load balancer is also disabled (
k3d.disableLoadbalancer: true)
-
-
Step 2: Create K3d cluster
K3D_FIX_MOUNTS=1 K3D_FIX_DNS=0 k3d cluster create -c k3d-config.yamlNote:
K3D_FIX_MOUNTS environment variable need to be set before executing k3d command. That makes / in the node containers
rsharedmounts fixing issues with Cilium installation. See details in this these k3d issues: #1268 and #479.K3D_FIX_DNS environment variable need to be set also, so K3d DNS fix that is executed by default is disabled.
Purpose of this DNS fix is to update defautl behaviour of DNS in docker. By default, containers use the Docker daemon’s embedded DNS resolver, which listens on the default DNS server IP address 127.0.0.11. This DNS server handles DNS queries from containers and forwards them to the appropriate DNS server for resolution.
K3D_FIX_DNS variable makes k3d to execute a fixing script that modifies /etc/resolv.conf in the container to point to host IP address, so host stub DNS resolver can be used.
However, DNS fix (K3D_FIX_DNS=1) breaks DNS resolution for external domain names (Internet)”: See details in open k3d issue: #1515
-
Step 3: Check cluster is running
kubectl get nodes
Installing Cilium CNI
Installation using Helm (Release 3):
-
Step 1: Add Cilium Helm repository:
helm repo add cilium https://helm.cilium.io/ -
Step2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update -
Step 4: Create helm values file
cilium-values.yml# Cilium operator config operator: replicas: 1 # Roll out cilium-operator pods automatically when configmap is updated. rollOutPods: true # Install operator on master node nodeSelector: node-role.kubernetes.io/master: "true" # Roll out cilium agent pods automatically when ConfigMap is updated. rollOutCiliumPods: true # K8s API service # K3s nodes running API proxy at port 6444 k8sServiceHost: 127.0.0.1 k8sServicePort: 6444 # Replace Kube-proxy kubeProxyReplacement: true kubeProxyReplacementHealthzBindAddr: 0.0.0.0:10256 # Configure IP Address Management mode. # https://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/network/concepts/ipam/ ipam: operator: clusterPoolIPv4PodCIDRList: "10.42.0.0/16" # Configure L2 announcements (LB-IPAM configuration) l2announcements: enabled: true externalIPs: enabled: true # Increase the k8s api client rate limit to avoid being limited due to increased API usage k8sClientRateLimit: qps: 50 burst: 200 # Istio configuration # https://docs.cilium.io/en/latest/network/servicemesh/istio/ # Disable socket lb for non-root ns. This is used to enable Istio routing rules socketLB: hostNamespaceOnly: true # Istio uses a CNI plugin to implement functionality for both sidecar and ambient modes. # To ensure that Cilium does not interfere with other CNI plugins on the node, cni: exclusive: false -
Step 5: Install Cilium in kube-system namespace
helm install cilium cilium/cilium --namespace kube-system -f cilium-values.yaml -
Step 1: Configure Cilium LB-IPAM
Create the following manifest file:
cilium-config.yaml--- apiVersion: "cilium.io/v2alpha1" kind: CiliumLoadBalancerIPPool metadata: name: "first-pool" namespace: kube-system spec: blocks: - start: "172.30.200.1" stop: "172.30.200.254" --- apiVersion: cilium.io/v2alpha1 kind: CiliumL2AnnouncementPolicy metadata: name: default-l2-announcement-policy namespace: kube-system spec: externalIPs: true loadBalancerIPs: trueApply the manifest file
kubectl apply -f cilium-config.yaml -
Step 6: Confirm that the deployment succeeded, run:
kubectl -n kube-system get pod
Note:
For details about Cilium installation and configuration see “Cilium CNI”