GitOps (ArgoCD)
Important: Deprecated Technology in PiCluster project
GitOps solution for the cluster has been migrated to FluxCD in release 1.9. ArgoCD technology has been deprecated and this documentation is not updated anymore.
Reasons behind this decission in PiCluster 1.9 release announcement.
See alternative GitOps solution documentation: “GitOps (FluxCD)”.
Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes.
It can be integrated with Git repositories, and used jointly with CI tools, like Jenkins or Github-actions to define end-to-end CI/CD pipeline to automatically build and deploy applications in Kubernetes.
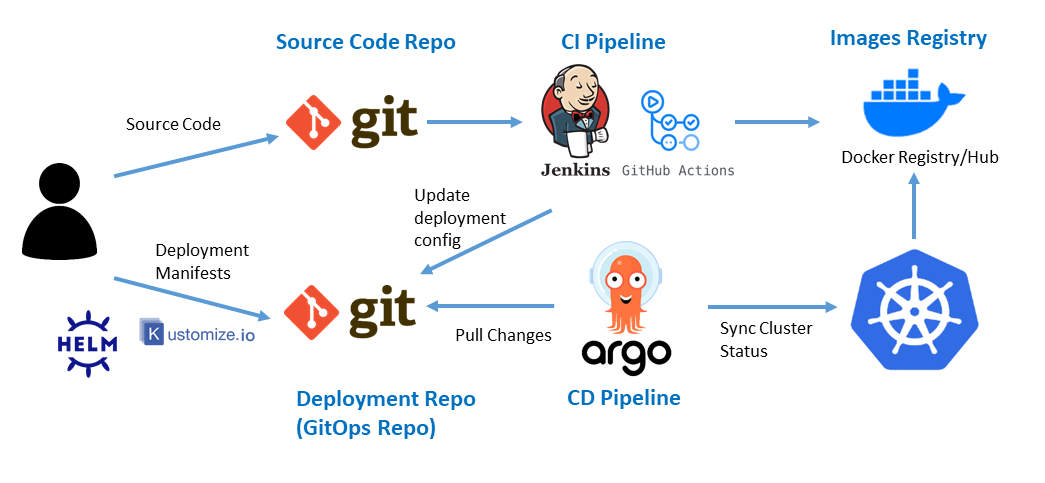
Argo CD follows the GitOps pattern of using Git repositories as the source of truth for defining the desired application state, through a set of kubernetes manifests. Kubernetes manifests can be specified in several ways:
- kustomize applications
- helm charts
- Plain directory of YAML/json manifests
Argo CD automates the deployment of the desired application states in the specified target environments (git repository). Application deployments can track updates to branches, tags, or pinned to a specific version of manifests at a Git commit.
ArgoCD installation
Helm Chart installation
ArgoCD can be installed through helm chart
- Step 1: Add ArgoCD helm repository:
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm - Step 2: Fetch the latest charts from the repository:
helm repo update - Step 3: Create namespace
kubectl create namespace argocd -
Step 4: Create argocd-values.yml
configs: params: # Run server without TLS # Ingress NGINX finishes TLS connections server.insecure: true cm: statusbadge.enabled: true # Adding Applications health check resource.customizations.health.argoproj.io_Application: | hs = {} hs.status = "Progressing" hs.message = "" if obj.status ~= nil then if obj.status.health ~= nil then hs.status = obj.status.health.status if obj.status.health.message ~= nil then hs.message = obj.status.health.message end end end return hs # Kustomize build options # --enable-helm: Enabling Helm chart rendering with Kustomize # --load-restrictor LoadRestrictionsNone: Local kustomizations may load files from outside their root kustomize.buildOptions: --enable-helm --load-restrictor LoadRestrictionsNone server: # Ingress Resource. ingress: ## Enable creation of ingress resource enabled: true ## Add ingressClassName to the Ingress ingressClassName: nginx # ingress host hostname: argocd.picluster.ricsanfre.com ## Default ingress path path: / pathType: Prefix # Enable tls. argocd-server-tls secret is created automatically for hostname tls: true ## Ingress annotations annotations: # Enable cert-manager to create automatically the SSL certificate and store in Secret # Possible Cluster-Issuer values: # * 'letsencrypt-issuer' (valid TLS certificate using IONOS API) # * 'ca-issuer' (CA-signed certificate, not valid) cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-issuer cert-manager.io/common-name: argocd.picluster.ricsanfre.comWith this config, Application resource health check is included so App of Apps pattern can be used. See below.
- Step 5: Install helm chart
helm install argocd argo/argo-cd --namespace argocd -f argocd-values.yml -
Step 6: Check Argo CD admin password
kubectl get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath='{.data.password}' -n argocd | base64 -d -
Step 7: Configure Port Forward
kubectl port-forward svc/argocd-server -n argocd 8080:80 --address 0.0.0.0 -
Step 8: Access Argo CD UI, using
adminuser and password obtained from step 6.http://<server-port-forwarding>:8080
Ingress Configuration
Igress NGINX will be used as ingress controller, terminating TLS traffic, so ArgoCD does not need to expose its API using HTTPS.
-
Configure ArgoCD to run its API server with TLS disabled
The following helm chart values need to be provided:
configs: params: # Run server without TLS # Nginx finishes TLS connections server.insecure: true -
For creating Ingress resource, add following lines to helm chart values:
# Ingress Resource. ingress: ## Enable creation of ingress resource enabled: true ## Add ingressClassName to the Ingress ingressClassName: nginx # ingress host hosts: - argocd.picluster.ricsanfre.com ## TLS Secret Name tls: - secretName: argocd-tls hosts: - argocd.picluster.ricsanfre.com ## Default ingress path paths: - / ## Ingress annotations annotations: # Enable cert-manager to create automatically the SSL certificate and store in Secret # Possible Cluster-Issuer values: # * 'letsencrypt-issuer' (valid TLS certificate using IONOS API) # * 'ca-issuer' (CA-signed certificate, not valid) cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: letsencrypt-issuer cert-manager.io/common-name: argocd.picluster.ricsanfre.com
See more details in Argo-CD Ingress configuration doc
Exclude synchronization of resources
Using automatic synchornization and pruning of resources might cause side effects with some of the kubernetes resources that are not created by ArgoCD.
See an example of this wrong behavior in issue #273. ArgoCD auto-synch policy is pruning VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent resources that are created automatically by backup process, making backup process to fail.
The way to solve this issue is to make ArgoCD to ignore the VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent resources during the synchronization process.
For doing that, ArgoCD need to be configured to exclude those resources from synchronization. See ArgoCD resource Exclusion for more details.
The following lines need to be added to helm chart:
configs:
cm:
## Ignore resources
# https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/operator-manual/declarative-setup/#resource-exclusioninclusion
# Ignore VolumeSnapshot and VolumeSnapshotContent: Created by backup processes.
resource.exclusions: |
- apiGroups:
- snapshot.storage.k8s.io
kinds:
- VolumeSnapshot
- VolumeSnapshotContent
clusters:
- "*"
ArgoCD Applications
ArgoCD applications to be deployed can be configured using ArgoCD UI or using ArgoCD specific CRDs (Application/ApplicationSet).
Different types of applications will be needed for the Pi Cluster
-
Directory Applications
A directory-type application loads plain manifest files from .yml, .yaml, and .json files from a specific directory in a git repository.
Using declarative Application CRD a directory application can be created applying the following manifest file
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: Application metadata: name: test-app spec: destination: namespace: <target-namespace> server: https://kubernetes.default.svc project: default source: # Enabling Recursive Resource Detection directory: recurse: true # Repo path path: test-app # Repo URL repoURL: https://github.com/<user>/<repo>.git # Branch, tag tracking targetRevision: HEAD syncPolicy: # Automatic sync options automated: prune: true selfHeal: trueWhere:
destination.namespace: namespace to deploy the applicationdestination.server: cluster to deploy the application (https://kuberentes.default.svcindicates local cluster)source.repoURLis the URL of the Git Repositorysourcepathis the path within the Git repository where the application is locatedsource.targetRevisionis the Git tag, branch or commit to tracksyncPolicy.automatedare ArgoCD auto-sync policies, to automatically keep in synch application manifest files in the cluster, delete old resources (pruneoption) and launch sych when changes are made to the cluster (selfHealoption)
-
Helm Chart Applications in ArgoCD
Helm chart applications can be installed in a declarative GitOps way using ArgoCD’s Application CRD.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: Application metadata: name: cert-manager namespace: argocd spec: project: default source: chart: cert-manager repoURL: https://charts.jetstack.io targetRevision: v1.10.0 helm: releaseName: cert-manager parameters: - name: installCRDs value: "true" # valueFiles: # - values.yaml destination: server: "https://kubernetes.default.svc" namespace: cert-managerWhere:
chartis the name of the chart to deploy from the Helm Repository.repoURLis the URL of the Helm Repository.releaseNameis the version of the chart to deployparameters- Helm chart parameters (overrriding values in values.yaml file)
Alternatively, to provide individual parameters, a values file can be specified (
.spec.source.helm.valueFiles). -
Kustomize Application
Kustomize traverses a Kubernetes manifest to add, remove or update configuration options without forking. It is available both as a standalone binary and as a native feature of kubectl Kustomize can be used to over a set of plain yaml manifest files or a Chart.
Argo CD has native support for Kustomize and has the ability to read a kustomization.yaml file to enable deployment with Kustomize and allow ArgoCD to manage the state of the YAML files.
A directory type application can be configured to apply kustomize to a set of directories just deploying in the directory (
source.path) akustomize yamlfile.apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: Application metadata: name: test-app namespace: argocd spec: destination: namespace: argocd name: in-cluster source: path: <path-to-kustomization.yaml-file> repoURL: https://github.com/<user>/<repo>.git targetRevision: master syncPolicy: automated: prune: true selfHeal: trueTo provide build options to kustomize,
kustomize.buildOptionsfield of argocd-cm ConfigMap need to be configured.The following kustomize build options have been added through helm chart values.yaml
-
Using kustomize with helm chart inflation
Kustomize has support for helm chart inflation using
helm templatecommand.Note:
Not all
helm templateoptions are supported. ArgoCD community has the intention to support them all eventually. See kustomization helmChart documentation.kustomize
--enable-helmbuild option need to be added to support helm chart inflation. -
Enable local kustomizations to load files from outside their root folder.
Kustomize
--load-restrictor=LoadRestrictionsNonebuild option need to be added to support it.This build option is needed, when using helm chart inflation capability, to overwrite
values.yamlfile defined inbasedirectory with contents ofvalue.yamlfile defined in theoverlaysfolder.Kustomize’s
HelmChart.additionalFilesfield can be used jointly withHelmChart.valuesFilefor this purpose.
Chek out further details in Argo CD Kustomize applications documentation.
-
Helm Charts (Multiple source repos)
Since ArgoCD 2.6, multiples sources can be defined per Application. One of the most common scenarios for using multiple sources is for deploying 3rd party helm charts:
- Use an external/public Helm chart
- You want to override the Helm values with your own local values
- You don’t want to clone the Helm chart locally as well because that would lead to duplication and you would need to monitor it manually for upstream changes.
With this new functionality, definition of Umbrella Charts is not needed anymore.
Example of an Application is:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: cert-manager
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
sources:
- repoURL: https://charts.jetstack.io
targetRevision: v1.10.0
chart: cert-manager
helm:
releaseName: cert-manager
valueFiles:
- $values/charts/cert-manager/values.yaml
- repoURL: 'https://github.com/<user>/<repo>.git'
targetRevision: dev
ref: values
destination:
server: "https://kubernetes.default.svc"
namespace: cert-manager
In this case the Helm values is provided from a specific path within a specific repo.
Helm Umbrella Charts
Important: ArgoCD 2.6 introduced new functionality to support multiple source repos per Application. That new functionality removes the need of using Helm Umbrella Charts to deploy 3rd party helm charts.
See further details in “ArgoCD documentation: Multiple Sources for an Application”
ArgoCD Helm application, before release 2.6, had the limitation that helm Values file must be in the same git repository as the Helm chart.
If you wanted to deploy helm charts belonging to third party repositories, it was not possible to define your own helm values file located in your own repository to override the default set of values.
To enable this scenario Helm Umbrella design pattern had to be used.
Helm Umbrella chart is sort of a “meta” (empty) Helm Chart that lists other Helm Charts as a dependency (subcharts).
It consists of a empty helm chart in a repo directory containing only chart definition file (Chart.yaml), listing all subcharts, and its corresponding values.yaml file.
-
<repo-path>/Chart.yamlapiVersion: v2 name: certmanager version: 0.0.0 dependencies: - name: cert-manager version: v1.10.0 repository: https://charts.jetstack.io -
<repo-path>/values.yamlcert-manager: installCRDs: true
Using this pattern, ArgoCD directory-type application can be declarative deployed.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: umbrella-chart-app
spec:
destination:
namespace: <target-namespace>
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
project: default
source:
path: <repo-path>
repoURL: https://github.com/<user>/<repo>.git
targetRevision: HEAD
helm:
<additional helm options>
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
Argo CD looks for a Chart.yaml file under
helm template \
--dependency-update \
--namespace <target-namespace> \
<app-name> <repo-path> \
| kubectl apply -n <target-namespace> -f -
Additional options can be passed to helm command using .spec.helm parametes in Application resource.
helm.valueFiles: To specify the name of the values file (default values.yaml)helm.skipCRDs: To skip installation of CDRs defined in the helm chart
Kustomized Application using Helm Chart Inflator
As alternative to the use of Helm Umbrella charts, applications packaged with kustomized can be defined, using kustomized’s Helm inflator functionality. Kustomized uses helm template command to generate manifest files from a helm chart.
For using that functionality, helm chart details, can be specified within helmChart field in kustomized.yaml file.
Using Argo-cd’s kustomized applications with helm chart support has advantages over Argo-cd’s helm chart applications like ability to apply kustomized’s patches on the manifest files generated by the helm chart inflation process (execution of helm template command).
Kustomize application can have the following structure, including base configuration and different overlays (i.e patches), so helm chart values.yaml defined in the base can be patched (overwritten) by values.yaml in the overlays.
└── app-test
├── base
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── ns.yaml
│ ├── values.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── values.yaml
└── prod
├── kustomization.yaml
└── values.yaml
base/kustomize.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ns.yaml # Name service definition manifest file or any other
overlays/dev/kustomize.yaml and overlays/prod/kustomize
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
resources:
- ../../base
helmCharts:
- name: <helm-chart-name>
repo: <helm-chart-repo>
version: <helm-chart-version>
releaseName: <release-name>
namespace: <namespace>
valuesFile: ../../base/values.yaml
includeCRDs: true
additionalValuesFiles:
- values.yaml
base helm values.yaml file (base/values.yaml) is used as main values file (helmCharts.valueFile). This values.yaml file is merged with values.yaml defined in the overlay directory (overlay/x/values.yaml) using (helmCharts.additionalValuesFiles)
This helm chart could be installed executing the following command:
kubectl kustomize --enable-helm --load-restrictor=LoadRestrictionsNone app/overlay/dev | kubectl apply -f -
The previous command will apply the dev overlay to inflate helm chart, using overlay values.yaml to overwrite default values provided in base and patch them after the inflation.
Warning:
Using kustomize, manifest files are generated via helm template command. This is the same procedure used by ArgoCD when installing a HelmChart application, so the output should be the same.
Applying kustomize manifest files directly could provoke undesired results, in case that inflated helm chart contains helm hooks, only processed by helm install or helm upgrade commands but not by kubectl kustomize <options> <path> | kubectl apply -f - command.
ArgoCD, is processing helm hooks annotated resources, and translate them into ArgoCD hooks, so the functionality provided by the helm hooks is not lost. See ArgoCD helm hooks support.
Bootstraping the cluster using App of Apps pattern
For bootstraping the cluster app of apps pattern can be used. The App-of-Apps design is basically an Argo CD Application made up of other Argo CD Applications.
It consist of a ArgoCD application, (root application) containing a set of Application manifest files.
Syncwaves can be used to specify the order in which each application need to be deployed.
Syncwaves and Synchooks are a way to order how Argo CD applies individual manifests within an Argo CD Application. The order is specified by annotating the object (argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave annotation) with the desired order to apply the manifest. Sync-wave is a integer number (negative numbers are allowed) indicating the order. Manifest files containing lower numbers of synch-waves are applied first.
All resources belonging to same sync-wave have to report healthy status before ArgoCD decices to apply next sync-wave.
Argo CD has health checks for several standard Kubernetes objects built-in. These checks then are bubbled up to the overall Application health status as one unit. For example, an Application that has a Service and a Deployment will be marked “healthy” only if both objects are considered healthy.
There are built-in health checks for Deployment, ReplicaSet, StatefulSet DaemonSet, Service, Ingress, PersistentVolumeClaim, etc. Custom health checks can be defined. See ArgoCD documentation - Resource Health
As described in the documentation, ArgoCD removed Application CRD health check from release 1.8. If App of Apps pattern is used Application health status check need to be added to ArgoCD configuration.
resource.customizations.health.argoproj.io_Application: |
hs = {}
hs.status = "Progressing"
hs.message = ""
if obj.status ~= nil then
if obj.status.health ~= nil then
hs.status = obj.status.health.status
if obj.status.health.message ~= nil then
hs.message = obj.status.health.message
end
end
end
return hs
Root App
In ArgoCD, the following App of Apps will be defined
root-app
├── infra
│ ├── cert-manager
│ └── external-secrets
└── app
├── app1
└── app2
- root-app: Root application: containing two other apps-of-apps:
- infra: Infrastructure related applications (i.e.: cert-manager, longhorn, minio, kube-prometheus-stack, etc.)
- apps: Microservice architecture support services (i.e.: kafka, databases, etc.) and self-develop applications.
root-app application will be specified as a kustomized application containing manifest resources files corresponding to ArgoCD Application.
Within git repo the following directory structure can be created
└── root-app
├── base
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── application.yaml
│ ├── infrastructure.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── patches.yaml
└── prod
├── kustomization.yaml
└── patches.yaml
-
base/kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1 kind: Kustomization resources: - infrastructure.yaml - application.yaml -
base/infrastructure.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: Application metadata: name: infrastructure namespace: argocd finalizers: - resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io annotations: argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "-2" spec: project: picluster source: path: kubernetes/bootstrap/infra/overlays/prod repoURL: https://github.com/ricsanfre/pi-cluster targetRevision: master destination: namespace: argocd name: in-cluster syncPolicy: automated: selfHeal: true prune: true retry: limit: 10 backoff: duration: 1m maxDuration: 16m factor: 2 syncOptions: - CreateNamespace=true - ServerSideApply=true - ApplyOutOfSyncOnly=true -
base/application.yaml
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: Application metadata: name: apps namespace: argocd finalizers: - resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io annotations: argocd.argoproj.io/sync-wave: "-1" spec: project: picluster source: path: kubernetes/bootstrap/apps/overlays/prod repoURL: https://github.com/ricsanfre/pi-cluster targetRevision: master destination: namespace: argocd name: in-cluster syncPolicy: automated: selfHeal: true prune: true retry: limit: 10 backoff: duration: 1m maxDuration: 16m factor: 2 syncOptions: - CreateNamespace=true - ServerSideApply=true - ApplyOutOfSyncOnly=trueBoth applications are configured to be synchronized using different waves. So
infrastuctureapp of apps will be deployed beforeappsapp of apps.infrastructureandappsapplications point to a different repository path, containing another kustomized application following the app of apps pattern (manifest files are argoCD Application) and its folder structure is similar to the one used byroot-app
Tip:
Example of this structure can be found in an old version of the repo. Checkout /kubernetes (release 1.8.9)
-
Root application created for Pi-Cluster can be found in /kubernets/bootstrap/root-app (release 1.8.9).
-
Infrastructure app of apps can be found in /kubernets/bootstrap/infra (release 1.8.9).
-
Applications app of apps can be found in /kubernets/bootstrap/apps (release 1.8.9).
Deploying Root application
Root application can be deployed declarative applying the following manifest file:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: root
namespace: argocd
finalizers:
- resources-finalizer.argocd.argoproj.io
spec:
project: picluster
source:
path: kubernetes/bootstrap/root-app/overlays/prod
repoURL: https://github.com/ricsanfre/pi-cluster
targetRevision: master
destination:
namespace: argocd
name: in-cluster
syncPolicy:
automated:
selfHeal: true
prune: true
retry:
limit: 10
backoff:
duration: 1m
maxDuration: 16m
factor: 2
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
This can be done executing the following command from repo home directory
kubectl kustomize --enable-helm --load-restrictor=LoadRestrictionsNone \
kubernetes/bootstrap/argocd/overlays/prod | kubectl apply -f -
CRDs Application
Application containing all CRDs could be created and deployed in the first sync-wave. So all other applications making use of CRDs can be deployed with success even when the corresponding Controller services are not yet deployed. For example: Deploying Prometheus Operator CRDs as part of a CRDs Application, allows to deploy prometheus monitoring objects (ServiceMonitor, PodMonitor, etc) for applications that are deployed before kube-prometheus-stack application.
Tip: For an example of such CRDs application, check out /kubernetes/infraestructure/crds. Old ArgoCd applications in the repository.
Repo Structure
The Git repo structure containing all application manifest files is the following
kubernetes
├── apps # end user applications
├── bootstrap # cluster bootstraping
│ ├── apps # argo-cd end-user applications (end-user Application resources)
│ ├── argocd # argoc-cd bootstraping (root-app app of apps definition)
│ ├── infra # argo-cd infraestructure apps (infrastructure Application resources).
│ ├── root-app # argo-cd root application (infra and apps manifest files)
│ └── vault # vault bootstraping manifest files
└── infrastructure # infrastructure applications
Tip:
Example of this structure can be found in an old version of the repo. Checkout /kubernetes (release 1.8.9)